Summary
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a skin condition that arises from the body’s exaggerated immune response to a wide range of agents acting on the skin from the outside or from within the body. Examples of agents that act externally include chemicals and drugs. Internally acting factors, such as the body’s hypersensitivity to various antigens (toxic or foreign substances) and haptens (a type of antigen) can also lead to eczema. In general, the symptoms of eczema include itching, redness with swelling, oozing, and scaling of the skin. The treatment options for eczema, as well as the prognosis, vary with the type of eczema and the age of a person.

 Doctors for Eczema
Doctors for Eczema  OTC Medicines for Eczema
OTC Medicines for Eczema
 Eczema articles
Eczema articles News for Eczema
News for Eczema
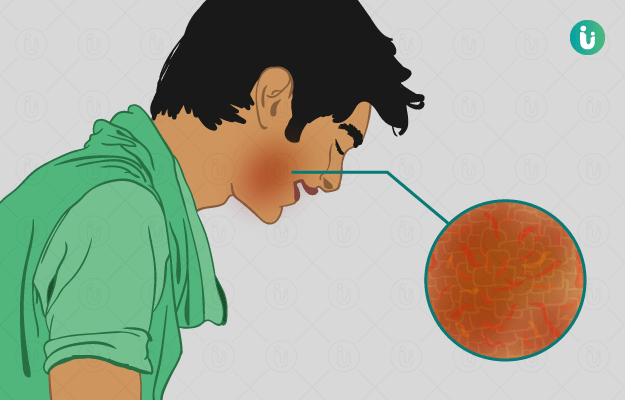
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Eczema
Ayurvedic Treatment of Eczema
 Home Remedies for Eczema
Home Remedies for Eczema
 Homeopathic Treatment of Eczema
Homeopathic Treatment of Eczema
 Yoga for Eczema
Yoga for Eczema


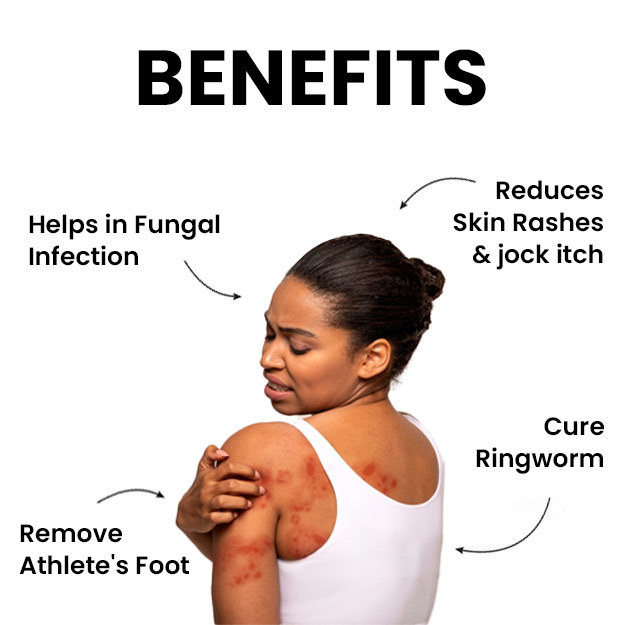
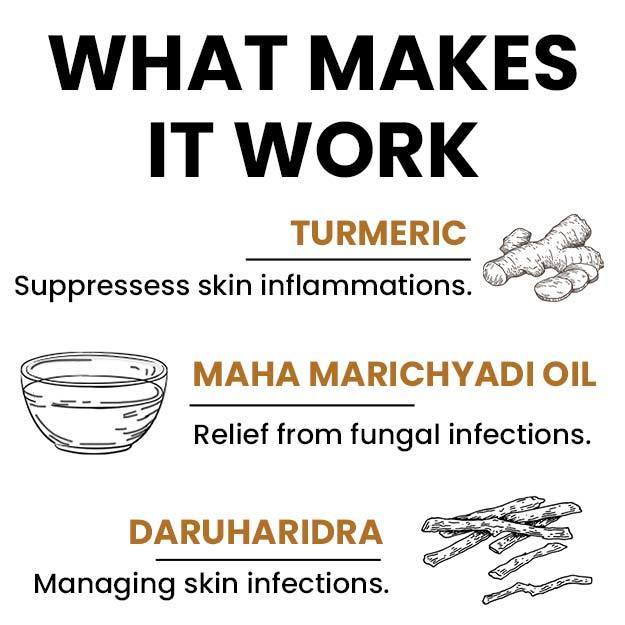
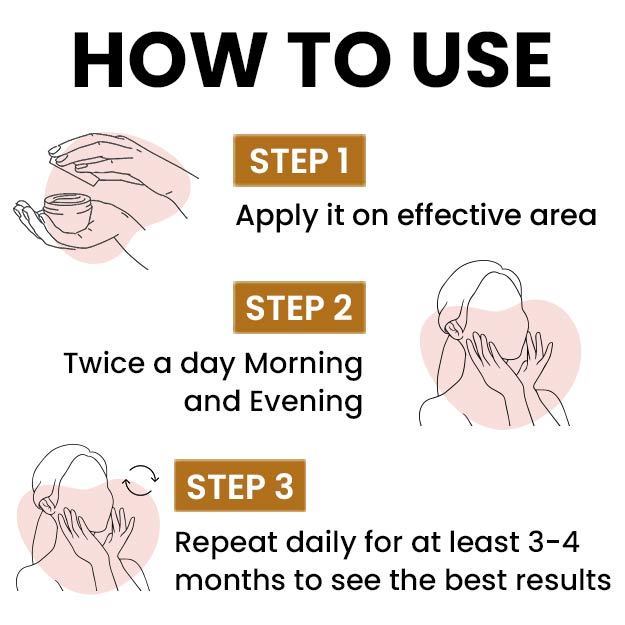










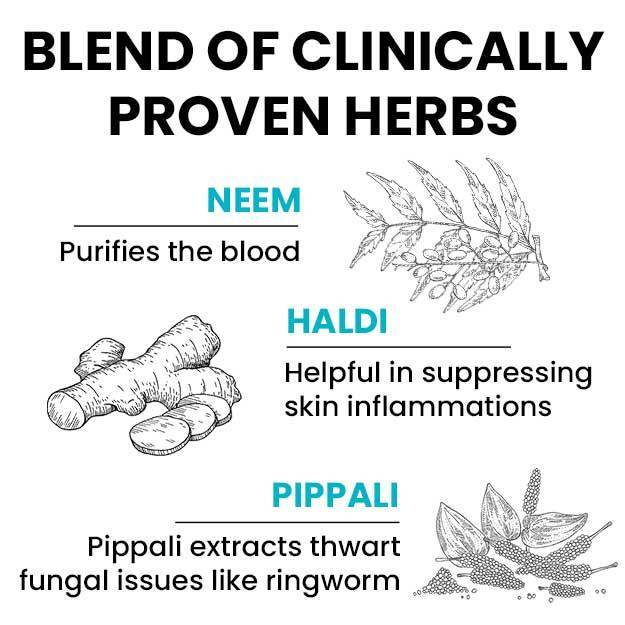


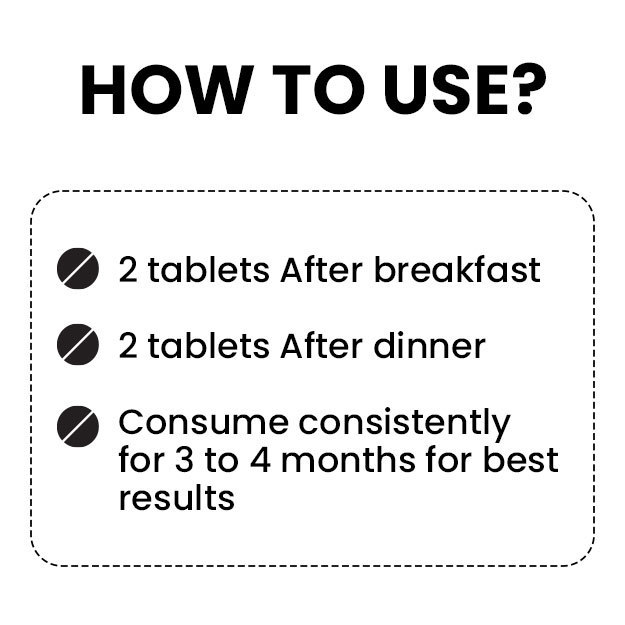






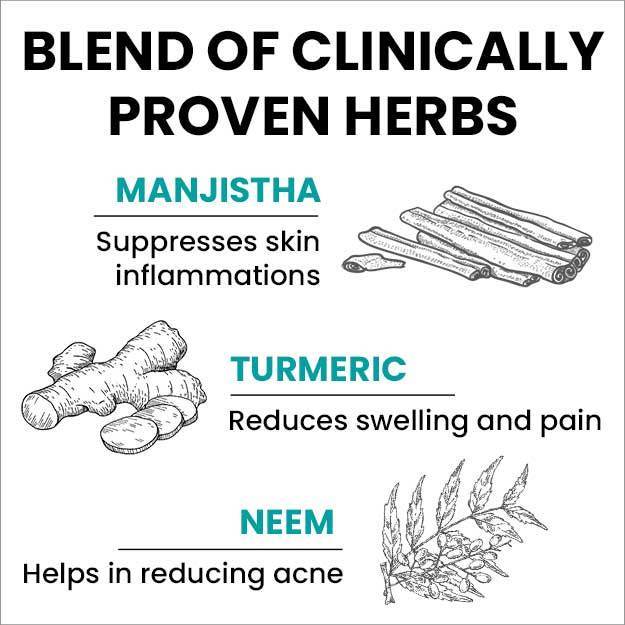











 Editorial Team
Editorial Team



 Dr. Medhavi Agarwal
Dr. Medhavi Agarwal

 Dr. Apratim Goel
Dr. Apratim Goel












