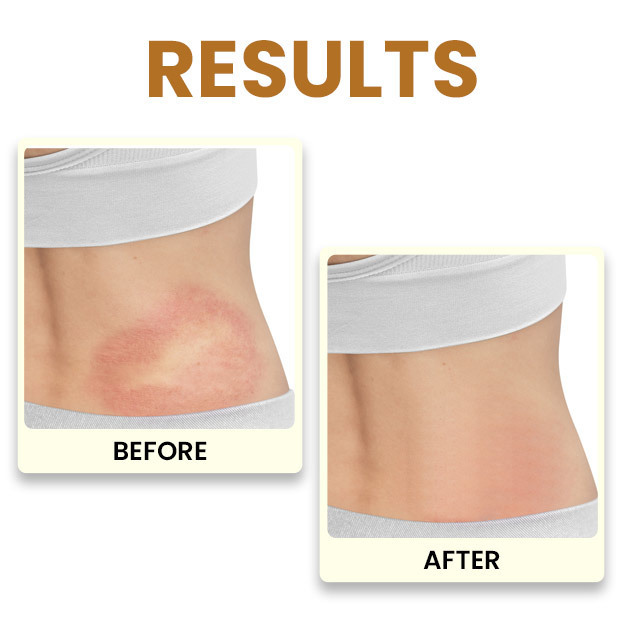
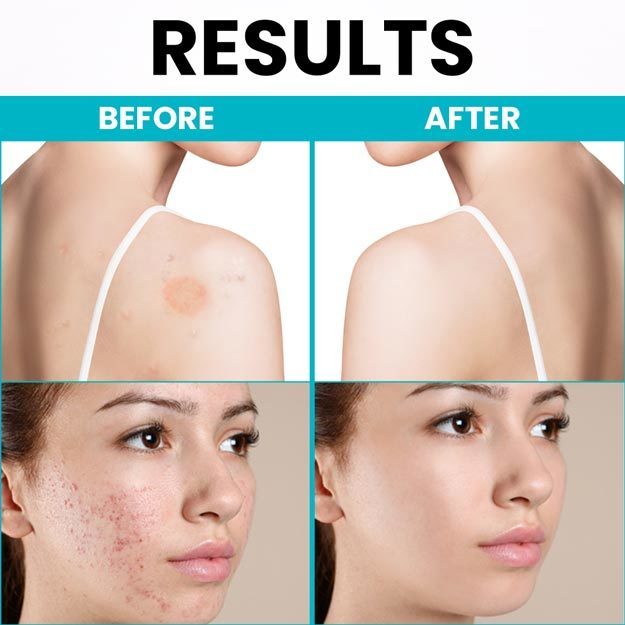
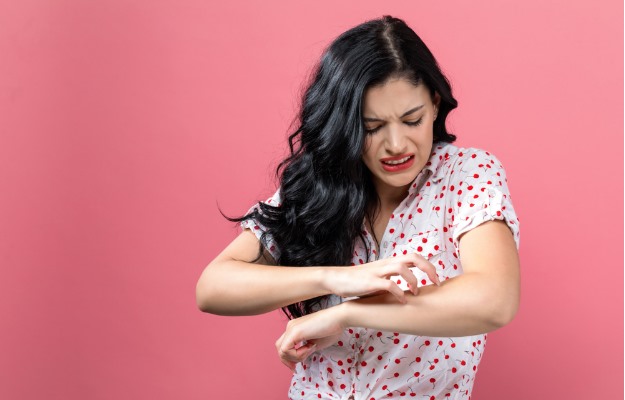
Eczema is a non-contagious, chronic inflammation of the skin. It is also called atopic dermatitis, atopic eczema, and allergic eczema and is characterized by a dry, red, scaly, and itchy rash on the skin that can sometimes lead to the formation of water or pus-filled blisters that secrete fluid when ruptured. Individuals suffering from eczema are also predisposed to skin infections due to bacteria, fungus, and virus. Though eczema is more common in babies and children, it can affect adults as well. According to an estimate, about 15% children and 2-4% adults in the world suffer from this condition.
The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but both genetic and environmental factors are said to play a role in the development of this condition. It has been reported that patients with eczema have an over-reactive immune system, which when triggered by various factors results in the characteristic inflammatory symptoms. Another possible reason for this condition is the mutation of a gene that produces a protein known as filaggrin, which is required to maintain the outer layer of the skin. This causes the skin to lose moisture, which makes it easier for environmental irritants or pathogenic microbes to cross the skin barrier. Other triggering factors for eczema include allergies, cold and dry air, fabrics made of wool, stress, UV radiation, perfumes, soaps or chemical irritants. Genetic inheritance of eczema has also been observed.
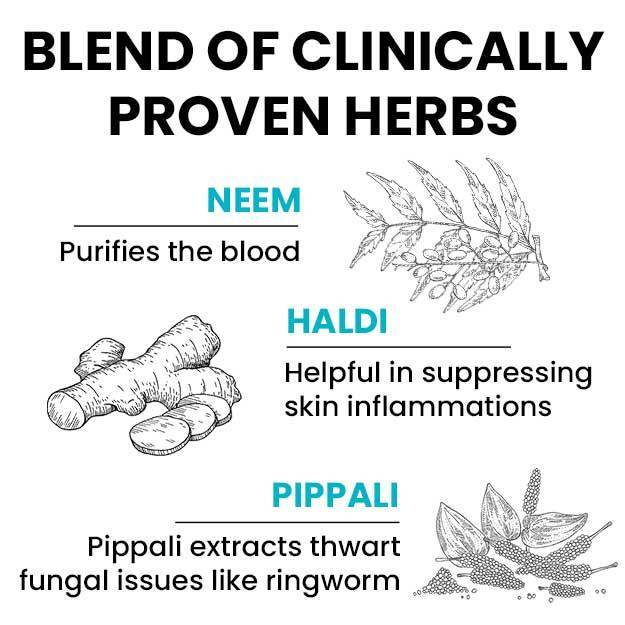
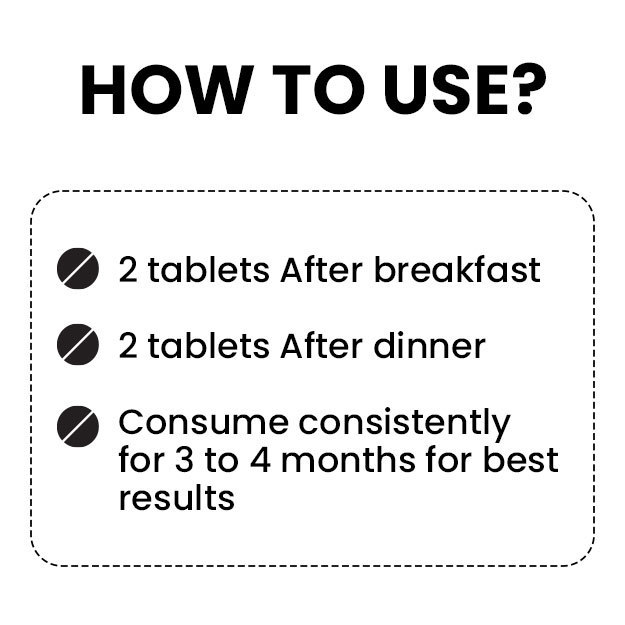
Conventional treatment for eczema involves the use of emollients to treat dry skin and topical corticosteroids to reduce swelling, as well as, redness.
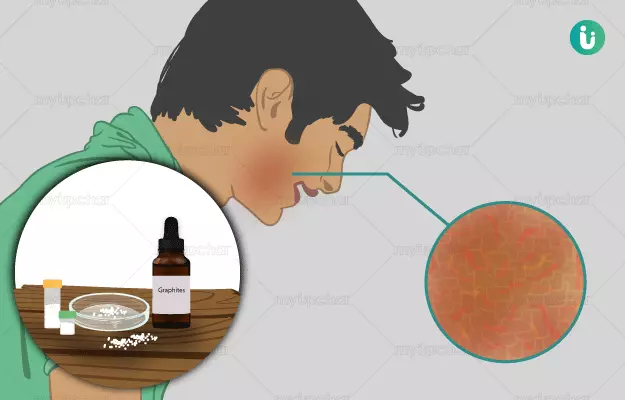
On the other hand homeopathic treatment aims treats each patient uniquely and aims at curing the underlying cause of the disease instead of suppressing symptoms. Few homeopathic remedies that are often indicated in the treatment of eczema are arsenicum album, calcarea carbonica, graphites, mezereum, natrium muriaticum, petroleum, rhus toxicodendron, and sulphur.