Did you know that constant high blood glucose levels actually damage and affect vital organs and parts of the body? That is why doctors and family members who care for you insist that you manage diabetes daily, constantly, and effectively, and avoid diabetes-induced coexisting chronic health conditions. Studies also suggest that people living with diabetes for a long time (15-20 years) often live with comorbid conditions arising due to diabetes. Let us explore the various body parts which are affected when diabetes is uncontrolled.
Eyes
Due to uncontrolled diabetes especially in people living with type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes the nerves in the eyes get affected mostly because of the autoimmune-mediated responses which attack healthy nerve cells leading to various complications in the eyes such as diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, diabetic macular edema, cataract and even serious conditions like vision loss.
- Diabetic retinopathy - this is a condition in which the retinal blood vessels present in the eyes get affected they begin to excessively dilate (expand) and leak internal fluids present inside the cells. It can also cause internal bleeding, clots resulting in distorted vision, and even vision loss.
- Glaucoma - is a condition in which the optic nerves which are connected to the brain cells get damaged due to pressure exerted inside the eye muscles. Glaucoma can occur in people without diabetes also but research claims that diabetes increases the risk of contracting glaucoma to manifolds when diabetes is not properly managed.
- Cataract - is a common eye condition in which the natural lens of the eye gets a thin layer formation which results in poor vision. Studies suggest people with diabetes are 5 times more prone to have cataracts than people without diabetes
- Diabetes macular edema - is a condition which is a progressive form of diabetes retinopathy characterized by inflammation (swelling) in the macula region present in the retina of the eyes.
Doctors highly recommend getting your eyes checked every six months if you have diabetes. Any symptoms such as dryness, excess watering, itching, redness, or distorted vision are not to be ignored and reported to your doctor without any further delay.
Oral Health
Uncontrolled and poorly managed diabetes not only leads to various nervous diseases but also invites infections, affecting membranes, gums, and enamel leading to various gums and tooth problems. The high glucose (sugar) levels pose a risk to your oral cavity which includes jaws, teeth, mouth area, tongue, and overall oral health. Bacterial and other pathogenic invasions in the mouth lead to following diseases such as gingivitis, periodontitis, candidiasis, pyorrhea, bad breath, and conditions like a dry or burning mouth.
You are recommended to maintain proper oral hygiene and brush twice a day at least to prevent plaque formation. Plaque is caused due to glucose present in the saliva mixed with food particles which coat and form a layer in our teeth. This layer is found to be bacteria-friendly and leads to diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis. Additionally, you are cautioned to visit a dentist immediately if there are any wounds or ulcers which are not healing for more than 5-7 days. A routine six-monthly dentist checkup is a must for people living with diabetes.
Heart
People with diabetes are 3-4 times more at risk of developing heart diseases such as strokes and cardiovascular diseases than people without diabetes. This is because studies claim that those having diabetes (with special reference to type 2 people) often also have high blood pressure, high levels of cholesterol, high levels of triglycerides, and obesity which make them twice as susceptible to suffering from heart attacks or strokes.
Medical investigations are suggestive that in due course of time diabetes weakens the heart muscles, blood vessels, and nerves in the surrounding regions which eventually leads to heart diseases. Having uncontrolled diabetes (high erratic blood glucose levels) along with high triglycerides (fats) makes the chances of having heart-related problems.
Doctors recommend a complete change of lifestyle, eating habits, and cutting down on alcohol and tobacco intake. This will not only help you in keeping your blood glucose (sugar) levels in check but also prevent you from various heart ailments.
Kidney and bladder
High blood glucose (sugar) levels pose a great threat to our body's filtration system (kidneys and bladder). As we all know that our kidneys help us remove all the waste and toxins from our body and pass it out via urine. With uncontrolled diabetes, the blood vessels of the kidneys are damaged which in turn affects the way our body cleanses our system. Research strongly hints diabetics must keep a check on their overall renal (kidney) health to avoid partial or complete kidney damage. Kidney function tests and urine tests must be routinely performed to detect protein and malfunctioning of the kidneys and bladder. Kidney damage could be a life-threatening condition if not detected at an early stage. Hence you are recommended to visit a doctor and report symptoms like frequent urination, especially at the night, difficulty during urination, reduced urine output or pain during urination, unusual ankle swelling, and albumin or protein detection in the urine at the earliest.
Sexual Health
It may come as a surprise to many but people living with diabetes, which includes both men and women undergo significant changes in their sex hormones adversely affecting their sexual health. Diabetes is emerging to be responsible for a number of sexual health-related issues amongst men causing erectile dysfunction, impotence, loss of libido, premature ejaculation, and delayed ejaculation. Substantial studies claim that 50 % of men who have had diabetes for more than 10-15 years suffer from erectile dysfunction. Studies also hint that men with erectile dysfunction are often found to also have a heart-related disorder such as coronary heart disease.
Women, on the contrary, have been observed to suffer from hormonal disbalances with special reference to type 2 diabetes. Diseases such as PCOS (Polycystic ovarian syndrome) are often interconnected with diabetes which is one of the major reasons for female infertility. Some other common conditions arising due to diabetes are vaginal dryness, lack of sexual desires, pain during sex, and arousal difficulties.
Both men and women are highly encouraged to consult a doctor and ask for solutions to ease agonies related to sexual health. There have been recent advances in medical technology and products (medications and therapies) that help overcome conditions like erectile dysfunction and infertility. However, doctors advise good control of blood glucose levels along with regular exercising are recommended for diabetics to avoid sexual health complications such as erectile dysfunction and infertility. However, doctors advise good control of blood glucose levels along with regular exercising are recommended for diabetics to avoid sexual health complications.
Mental Health
Psychologists suggest, that people living with diabetes often undergo emotional turmoils due to long-term conditions and chronic symptoms. Their mental health and well-being are equally important just as their physical well-being. Research hints people who are happy and content with their lives have proven to achieve good control of diabetes versus people who are unhappy. Scientists claim that with the onset of diabetes feelings of anger, guilt, depression, low self-esteem, and anxiety set in.
Doctors recommend family members and caregivers extend emotional support and motivate people with diabetes to maintain blood sugar levels responsibly. And most importantly do not let diabetes come in the way of your life.



 Doctors for Diabetes
Doctors for Diabetes  OTC Medicines for Diabetes
OTC Medicines for Diabetes
 Lab tests for Diabetes
Lab tests for Diabetes Diabetes articles
Diabetes articles News for Diabetes
News for Diabetes
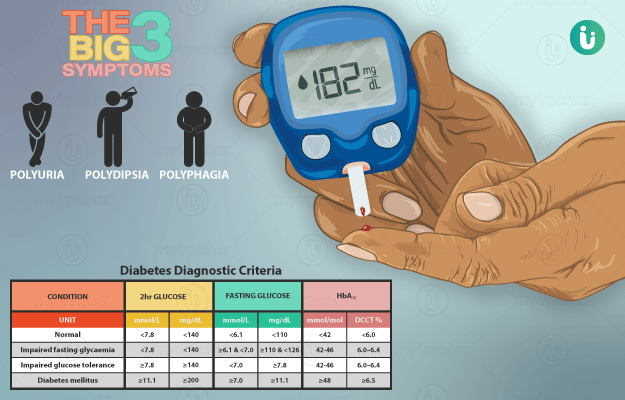
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Diabetes
Ayurvedic Treatment of Diabetes
 Home Remedies for Diabetes
Home Remedies for Diabetes
 Homeopathic Treatment of Diabetes
Homeopathic Treatment of Diabetes
 Yoga for Diabetes
Yoga for Diabetes




























 Editorial Team
Editorial Team
















