Summary
Sciatica refers to a painful condition caused by an injury to the sciatic nerve in the body. The symptoms include pain in the lower back accompanied by a numbness that radiates down one leg. It is mainly of two types – neurogenic and referred. The symptoms manifest suddenly and tend to be very unpleasant. There can be several factors which lead to sciatica. In most of the cases, sciatica is associated with a back injury or prolonged inactivity. Other causes include improper posture, obesity, neurological disorders, spondylitis, slipped disc, and muscle spasms. Sciatica resolves on its own within 4-6 weeks but if the symptoms persist then medical intervention becomes necessary. Sciatica can be treated by using pain-relief drugs, physiotherapy, massage, and in severe cases – surgery. Sciatica symptoms can be managed effectively by incorporating several lifestyle changes. However, it is essential to seek medical advice if symptoms relapse. Moreover, if left untreated, sciatica could result in complications such as increased pain and permanent nerve damage.

 Doctors for Sciatica
Doctors for Sciatica  OTC Medicines for Sciatica
OTC Medicines for Sciatica
 Lab tests for Sciatica
Lab tests for Sciatica Sciatica articles
Sciatica articles
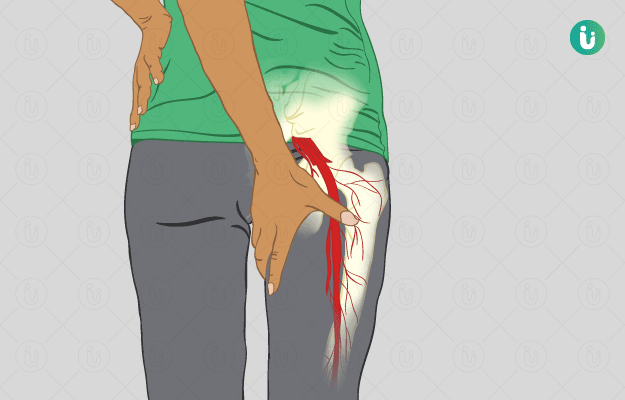
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Sciatica
Ayurvedic Treatment of Sciatica
 Diet for Sciatica
Diet for Sciatica
 Home Remedies for Sciatica
Home Remedies for Sciatica
 Homeopathic Treatment of Sciatica
Homeopathic Treatment of Sciatica
 Yoga for Sciatica
Yoga for Sciatica














 Editorial Team
Editorial Team




 Dt. Akanksha Mishra
Dt. Akanksha Mishra












