When you are in a stressful situation and your heart starts beating loudly, your hands start sweating and you start looking for a way to escape, if this has ever happened to you then you have experienced the real hormonal response called "fight-or-flight".
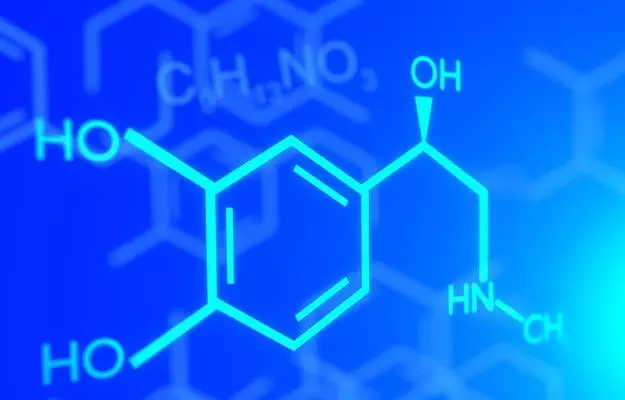
The "fight-or-flight" response is produced by a hormone called adrenaline. This hormone is an important part of the body's "fight-or-flight" response i.e. to prepare to fight or escape danger, but it can be harmful to our body if it happens too often. Because of this, it is very important for us to understand the adrenaline hormone.
Some people search around the world for things like bungee jumping, jumping off cliffs, diving, swimming in a cage with sharks to experience this response. However, not everyone is so enthusiastic.
But what exactly is adrenaline and what does it do in your body? It is important for you to know this. This article explains in detail what is adrenaline hormone? What are its functions and effects? And how does adrenaline hormone imbalance occur? And how to control it?
(Read more - Hormone Therapy: types, benefits)