What is Snake Bite?
Snakebite is a defensive mechanism of the snake to protect itself from predators. A snake bite may be due to a snake which is venomous. In this case, the poison may affect the nervous system, the heart or the blood-producing organs corresponding to symptoms that may be fatal if not treated in time. It has been found that the number of snake bites in India accounts for 1,00,000 cases and 45-50 thousand deaths yearly.
What are the main signs and symptoms?
Clinical signs and symptoms include:
- Fang spots on the wounds
- Blood oozing from the wound
- Oedema (swelling at the site of the bite and the limb)
- Colour difference in the affected region
- Dizziness
- Profuse sweating
- Sensation of a rapid heartbeat
- Increased heart rate
The venom may not pass into the bloodstream due to one of the following reasons:
- Lack of venom also known as ‘dry bite’
- Unable to bite due to protective clothing or shoes
- Venom leak in less severe cases
- Superficial attack not causing envenomation
What are the main causes?
Bites by snakes, such as king cobra, common krait, saw-scaled viper, and Russell’s viper are venomous bites.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
The most important treatment method involves the use of an anti-venom. The major issue or drawback is the lack of specificity. It is always advisable to consider snake bites as emergency cases since it is difficult to be sure whether the snake is venomous or not.
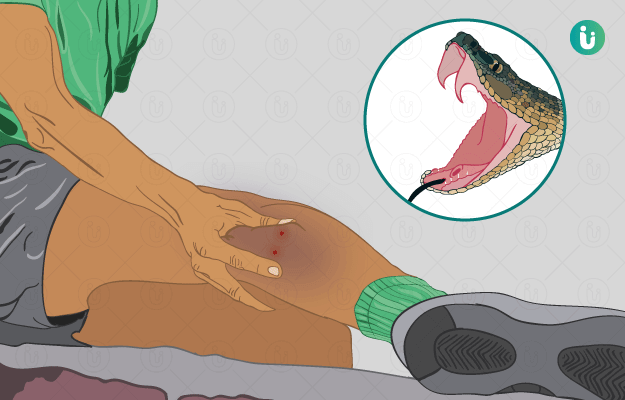
As first aid you can do the following:
- Ask the person who has been bitten to calm down and not panic, as this will only promote the spread of the poison rapidly into circulation
- Cover the bite with a dry, loose bandage or clothing
- Get to a centre that can deliver an anti-venom at earliest
- Do not tie a cloth or tourniquet close to the bite, this cuts off the circulation
- Do not wash the wound
- Do not use ice on the wound
- Do not try to suck the venom out of the wound
Snakebites can be prevented if you:
- Wear thick boots and long pants before venturing out or roaming in thick grasses
- Carry a torch or lamp at night
- Be cautious while moving any rocks or stones or collecting wood for cooking and while roaming in the mountain areas or swimming in small lakes and rivers
- Use appropriate repellents for snakes or rodents in storerooms or basements
- Do not attempt to catch a snake when motionless or when it appears to be dead
- Avoid keeping them as pets
- Always check your bed before sleeping and avoid sleeping on the floor
Snake bites may be prevented if appropriate measures and precautions are followed. This can reduce and prevent mortality and morbidity.

 OTC Medicines for Snake Bite
OTC Medicines for Snake Bite
 Snake Bite articles
Snake Bite articles
 First Aid for Snake Bite
First Aid for Snake Bite


 Dr. Srishti Gupta
Dr. Srishti Gupta











