Summary
Shortness of breath, medically known as dyspnea is a common health problem. It refers to a variety of perceptions experienced by a person, and some of the experiences are influenced by the person's emotional state. Since there is a wide range of causes that can lead to a shortness of breath, this makes the diagnosis of the exact cause a challenge. A rapid evaluation and diagnosis are critical to ensuring effective management. Sometimes, diagnosing the exact cause of dyspnea is very difficult to establish if there is more than one underlying disease. The various factors that can cause breathlessness include lung and heart disease, pneumonia, heart failure, acute coronary syndrome and other conditions like anaemia, obesity and mental disorders.

 Doctors for Shortness of Breath
Doctors for Shortness of Breath  OTC Medicines for Shortness of Breath
OTC Medicines for Shortness of Breath
 Lab tests for Shortness of Breath
Lab tests for Shortness of Breath Shortness of Breath articles
Shortness of Breath articles
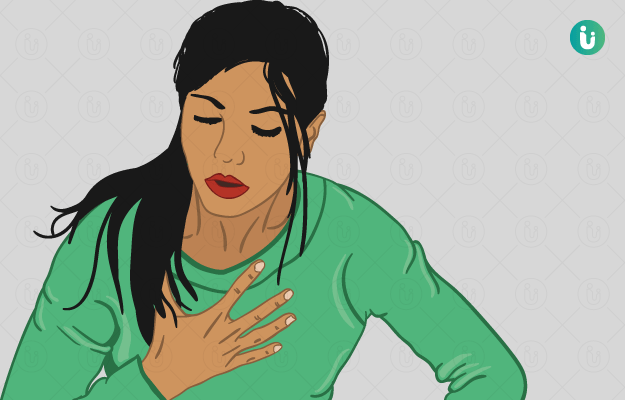

 Home Remedies for Shortness of Breath
Home Remedies for Shortness of Breath
 Homeopathic Treatment of Shortness of Breath
Homeopathic Treatment of Shortness of Breath




























 Editorial Team
Editorial Team
 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria











