Summary
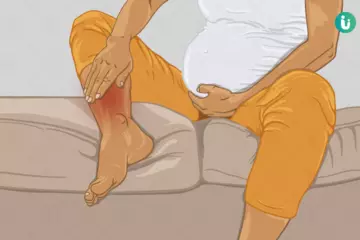
Hyperuricemia is a health problem in which there is an abnormally high level of uric acid in the body. Uric acid is formed in the body after the breakdown of proteins. When proteins are broken down, the chemical compound in them called purines are broken down into uric acid. There may be an increase in the uric acid levels due to three main reasons-an increased production of uric acid, a decreased excretion of uric acid, or a combination of these two mechanisms.
Hyperuricemia can be without any symptoms (asymptomatic) or it may have accompanying symptoms (symptomatic). There are many medical conditions that can result from an increase in the uric acid levels in the body along with accompanying symptoms. These include uric acid nephropathy (decreased kidney function due to high levels of uric acid in the urine), gout (urate crystal deposition in the joints due to high levels of uric acid circulating in the blood), and uric acid nephrolithiasis (uric acid kidney stones). When there are no accompanying symptoms with hyperuricemia, treatment is generally not recommended, but symptomatic hyperuricemia requires treatment as per the clinical presentation. Complications of hyperuricemia include gout, acute uric acid nephropathy, uric acid nephrolithiasis, and chronic renal insufficiency.

 Doctors for High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood
Doctors for High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood  OTC Medicines for High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood
OTC Medicines for High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood
 Lab tests for High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood
Lab tests for High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood articles
High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood articles
 Ayurvedic Treatment of High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood
Ayurvedic Treatment of High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood
 Homeopathic Treatment of High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood
Homeopathic Treatment of High Uric Acid Levels in the Blood

































 Editorial Team
Editorial Team


 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria

 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla