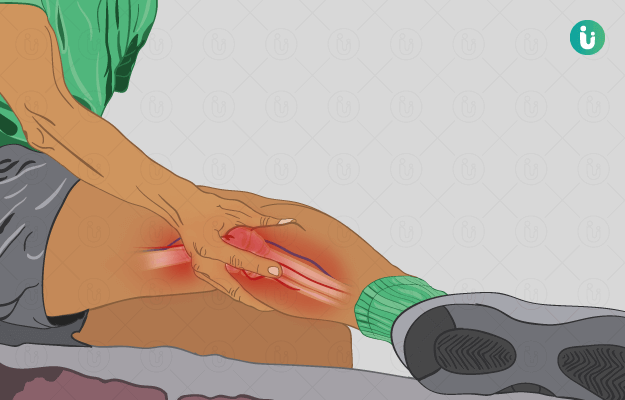
What is bone pain?
Bone pain is a symptom which manifests as an ache, tenderness or discomfort in one or more bones. Bone pain usually affects the long bones of the arms and legs. Although often overlooked, bone pain can drastically affect the normal functioning and daily life of a person.
What are its main associated signs and symptoms?
The characteristics of bone pain are associated with the underlying condition.
Bone pain associated with cancer:
- Initial tenderness in the affected region
- Constant or intermittent pain, even at rest
Bone pain associated with osteoporosis:
- Severe backache
- Change in posture
- Loss of height
- Impairment in one’s ability to walk
- Prolonged disability
Bone pain associated with arthritis:
- Reduction in joint flexibility
- Swelling of the joint
- Stiffness and deformity
- Reduced movement and function
Symptoms associated with Paget’s disease:
- Pain in the weight-bearing bones such as the spine, pelvis and legs
- Microfractures in the bone
Bone pain due to other causes may have additional specific symptoms relevant to the cause.
What are the main causes of bone pain?
The most common but less obvious cause of bone pain is bone cancer (primary cancer).
Other causes include:
- Osteoporosis
- Arthritis
- Paget’s disease
- Metastatic spread of cancer
- Impaired blood supply (as in sickle cell anaemia)
- Osteomyelitis
- Infection
- Injury or trauma, fracture post-accidents
- Leukaemia
- Overuse injury
- Toddler fracture (a stress fracture that occurs in toddlers)
How is it diagnosed and treated?
A thorough medical history and physical examination is a must for diagnosis of the underlying condition.
The following tests may be advised:
- Blood tests (such as complete blood count and differential blood count tests)
- Bone X-rays
- CT or MRI scan
- Hormone level studies
- Pituitary and adrenal gland function tests
- Urine analysis
Treatment of bone pain addresses both the symptom and the underlying disease. These include:
- Medications: Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, hormonal therapy, analgesics and laxatives for constipation after prolonged bed rest.
- Additional treatment measures for osteoarthritis may include:
- Topical pain-relieving creams
- Exercises and physical therapy
- Joint splinting or replacement therapy
- Treatment for osteoporosis and arthritis may also include:
- Exercises that work on stretching, strengthening, posture and range of motion
- Rehabilitation
- Additional treatment for Paget’s disease include:
- Medications to reduce the rate of bone remodelling
- Surgery may be required in certain cases for bone realignment or joint replacement
- Physical exercise to maintain bone strength and keep weight-bearing joints mobile and free of pain
- Treatment for bone cancer may include:
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Immunotherapy

 Doctors for Bone Pain
Doctors for Bone Pain  OTC Medicines for Bone Pain
OTC Medicines for Bone Pain
 Bone Pain articles
Bone Pain articles






 Editorial Team
Editorial Team












