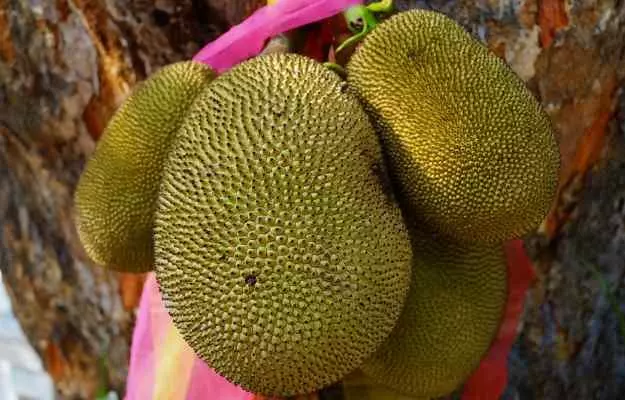
Jackfruit, commonly known as kathal, is a tree belonging to the Moraceae family. Its fruit is widely popular in tropical climates. It has a sweet taste when ripe and is fleshy on the inside. The fleshy part, also known as the bulb, can be eaten as such or used in various recipes. The fruit when still green in colour, ie unripe is remarkably similar in texture to chicken, which makes jackfruit a favoured vegetarian substitute for meat. Jackfruit is also canned in a brine solution which is sometimes referred to as vegetable meat.
The fruit has been popularly used in traditional Chinese medicine for various purposes.
The tree of jackfruit is about 50 to 60 feet in height and has a long lifespan, usually more than 100 years. It bears fruits in the rainy season between the months of May and August. A mature jackfruit tree can produce about to 100 to 200 fruits in a season. The fruits of the jackfruit tree are the largest tree-borne fruits and can weigh up to 55 kgs.
The ideal growing locations for the jackfruit tree are tropical lowlands. The tree is widely cultivated and is a popular food item throughout the tropical regions of the world. Jackfruit is a commonly used ingredient in South and South-east Asian cuisines. It is the national fruit of Sri Lanka and Bangladesh.
The state of Kerala in India is the largest producer of jackfruit in the world.
Some basic facts about jackfruit (kathal)
- Botanical Name: Artocarpus heterophyllus
- Family: Moraceae
- Common Name: Jack tree, fenne, jakfruit,
- Sanskrit Name: Kathal
- Parts Used: Fruits, seeds, fleshy flower petals
- Native Region and Geographical Distribution: Native to the tropical regions, especially South and South-east Asia