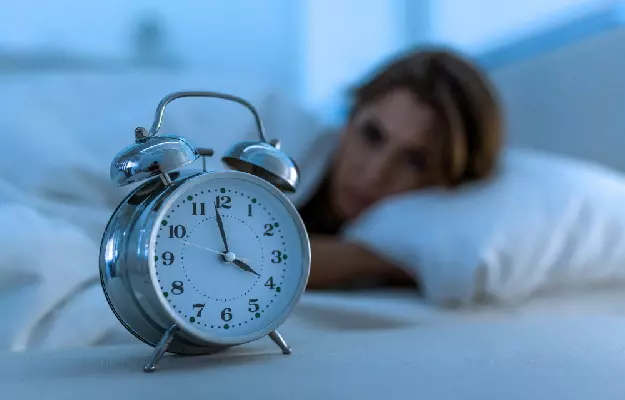
Biological rhythm is the natural cycle of changes in chemicals or functions present in our body. It's like an internal clock that coordinates other clocks in our body. The "clock" is located in the brain, just above the nerves that allow us to see. It is made up of thousands of nerve cells that help coordinate the functions and activities of our body. Overall, so that our body can do the right work at the right time, there is a clock running in our body which automatically sends us instructions to do the right work all the time. If it goes back and forth then the balance of the body gets disturbed and the body Can't work properly. The clock in our body also has different biological rhythms. Let us understand-
Read more - (First aid for asthma attack)
Our body clock has four biological rhythms:
Circadian Rhythm: It Controls The Work We Do In 24 Hours. Physiological And Behavioral Rhythms Such As Sleep
Diurnal Rhythm: It Is Synchronized With Day And Night With The Circadian Rhythm
Ultradian Rhythm: These Are The Rhythms That Send Instructions To Our Body For Sudden Actions And Have A Shorter Duration And Higher Frequency Than The Circadian Rhythm.
Infradian Rhythm: Biological Rhythm That Lasts More Than 24 Hours, Such As The Menstrual Cycle
The circadian clock plays a physiological, mental, and behavioral role in responding to light and darkness. This clock helps regulate the following functions including:
- Sleep
- Hunger
- Body Temperature
- Hormone Levels
- Daily Performance
- Blood Pressure
- Time To React To Things
Sometimes external factors can affect the biological rhythm. For example, exposure to sunlight, medications, and caffeine can cause trouble sleeping.
Read more - (What is normal body temperature?)