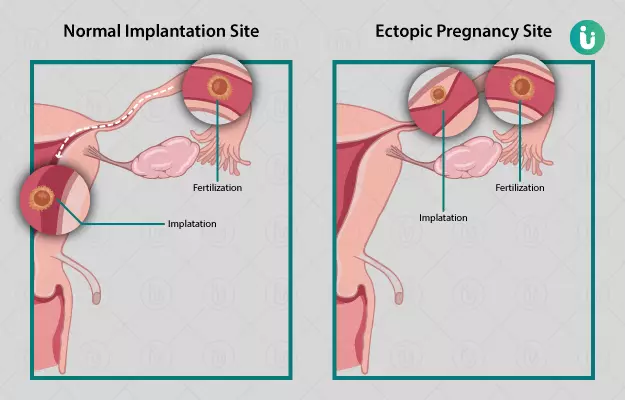
In normal pregnancies, the fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus after passing through the fallopian tube and the embryo develops inside the uterus. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg attaches somewhere other than the uterus (mostly in the fallopian tube). For this reason, it is sometimes also called "tubal pregnancy". Ectopic pregnancies can also occur in your ovaries.
Ectopic pregnancies are very rare. It is found in 2 out of 100 women. But if it is not treated on time, it can be very dangerous. During an ectopic pregnancy, when the stretch in the fallopian tube increases, it breaks, this is called a ruptured ectopic pregnancy. This can lead to internal bleeding, infection and sometimes even death.
Read further in this article what are the symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, why it happens and what is its treatment. Also, information about getting pregnant again after ectopic pregnancy has also been given.
(Read more - Blocked Fallopian Tubes)