Thyroid is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland (a gland that secretes the hormones directly into the bloodstream) located in the front part of the neck. It produces various hormones including Triiodothyronine (T3) and Tetraiodothyronine (Thyroxine) (T4), which help control the growth, development, and metabolism of body and calcitonin, which helps maintain bone mineral density.
The levels of thyroid hormones are regulated by a feedback cycle in our body. Hypothalamus (an endocrine gland) in the brain secretes Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which in turn causes the pituitary gland to secrete Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) that controls the release of T3 and T4 depending on their levels in blood.
When T3 and T4 levels in bloodstream fall below a certain level, TSH is released by the pituitary gland to secrete more thyroid hormones and in case of high levels of T3 and T4, TSH levels will be reduced.
Excess T3 and T4 levels in blood with low TSH levels are signs of an overactive thyroid gland indicating hyperthyroidism. On the contrary, low levels of T3 and T4 with elevated levels of TSH are manifestations of an underactive thyroid gland indicating hypothyroidism.
Apart from hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, other thyroid disorders include goitre, and thyroid nodules arising from cysts (fluid-filled areas in the thyroid), benign tumours (non-cancerous growths), and thyroid cancer.
Hypothyroidism can be caused due to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation of the thyroid gland), thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland), postpartum thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland after delivery), iodine deficiency, and a non-functioning thyroid gland in a new-born. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include weight gain, forgetfulness, fatigue, intolerance to cold, heavy or frequent menstrual periods, dry hair and skin, and hoarse voice.
Hyperthyroidism may result from Grave’s disease, toxic multinodular goitre, thyroid nodules, and over-consumption of iodine.
Iodine is an essential mineral responsible for the smooth functioning of thyroid gland and production of thyroid hormones. Goitre is an enlargement of thyroid gland that may occur due to iodine deficiency. Though, it may also appear as a symptom of hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, or due to some other causes like Grave's disease and side effects of certain medications. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism are weight loss, irritability, nervousness, tremors, muscular weakness, sleep disturbances, intolerance to heat, sleep disturbances, scanty or infrequent menstruation, and an enlarged thyroid gland.
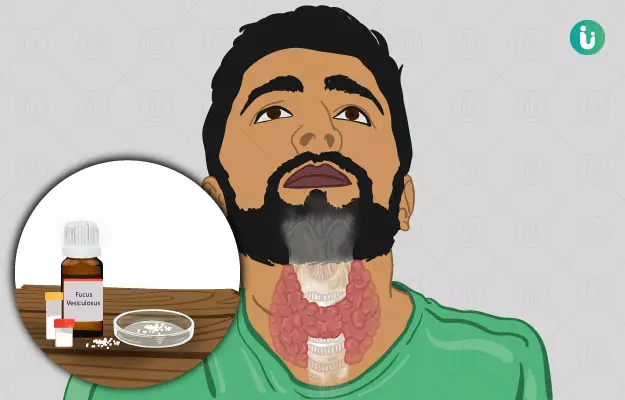
Homoeopathic treatment stimulates the body to restore hormonal imbalance. Homeopathic remedies that are used for the treatment of thyroid disorders includes, iodine, fucus vesiculosa, calcarea carbonica, bromium, spongia, natrium muriaticum, thyroidinum etc. These remedies are prescribed after considering individual characteristics of a patient’s personality and physiology.
Troubled by obesity? Failed to lose weight? Now control weight easily by myUpchar Ayurveda Medarodha Weight Control Tablet. Get started today and take steps towards a healthy life.