What is rheumatic fever?
Rheumatic fever is a complication that develops due to inadequately treated or untreated streptococcal infection of the throat. It can cause severe illness of the skin, the heart, the joints, and the brain. The infection mainly affects children between the ages of 5 to 15 years. Rheumatic fever usually occurs 14 to 28 days after the onset of streptococcal throat infection.
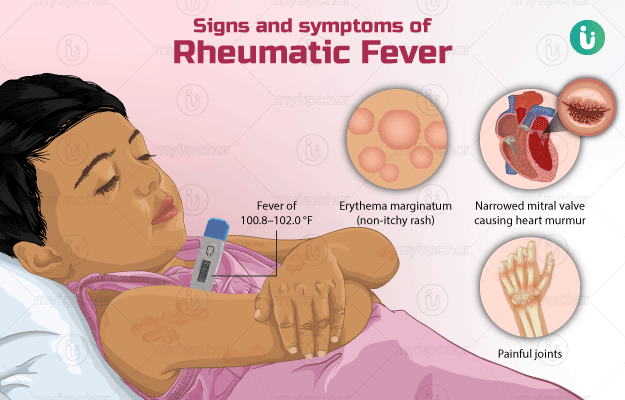
What are its main signs and symptoms?
The signs and symptoms of rheumatic fever include:
General
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
- Pain in the abdomen or chest
- Symptomless heart problems
- Bleeding from nose
- Unusual crying or laughing bouts indicating loss of emotional control
Joints related changes:
- Red, hot, painful, and swollen joints (especially wrists, ankles, knees, and elbows)
Skin-related changes:
- Lumps or nodules on the skin
- Rash, especially on the trunk and upper part of the arms or the legs which could look like a snake or be ring-shaped.
- Sydenham chorea a neurological condition is characterised by quick, jerky movements affecting the hands, feet, and the face.
What are the main causes?
The main cause of rheumatic fever is group A streptococci infection (Streptococcus pyogenes). The infection causes an abnormal autoimmune response (to streptococcus throat infection or scarlet fever) in a host who is genetically susceptible.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
After taking a history of symptoms, the physician will thoroughly examine the skin and the joints and will check for heart sounds, followed by advising the following tests:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR – to check for inflammation)
- Anti-streptolysin O (ASO) blood test to check for repeated infection
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Evaluation of fixed major and minor criteria (Jones criteria)
Management of Rheumatic fever includes:
- For infections, antibiotics are prescribed, which might be advised for a long term to prevent recurrence (For children, it is advised till 21 years of age, sometimes even lifetime).
- Medications such as aspirin or corticosteroids are given to relieve symptoms like swelling and inflammation.
- Medications for seizures are prescribed when an individual exhibits abnormal movements or behaviour.

 OTC Medicines for Rheumatic Fever
OTC Medicines for Rheumatic Fever