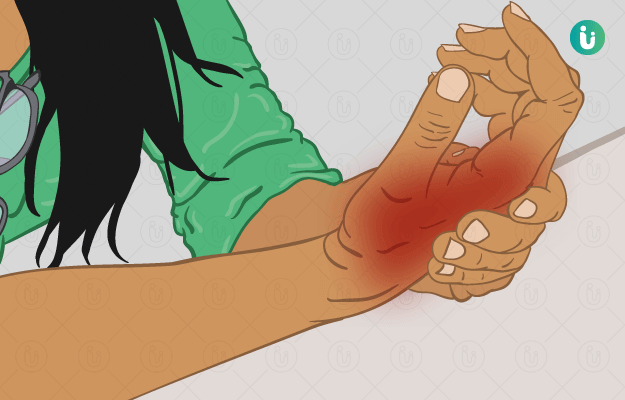
What is hand pain?
Pain in the hand can be mild or severe and, at times, can be disabling enough to prevent a person from performing daily activities. In a majority of the cases, this pain may be an expression of a disease, and treating the underlying cause usually settles the pain.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Inflammation, injury, nerve damage, chronic health conditions (like deficiencies, hyperuricemia), sprain or fracture of any of the multiple ligaments and bones in the hand can lead to hand pain. Symptoms of hand pain vary according to the type of pathology involved and the structures affected; however, some common signs and symptoms of hand pain are:
- Pain (throbbing, tingling, cramp-like)
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Tingling or numbness
- Inability or difficulty in hand movements or performing activities with the affected hand
What are its main causes?
Hand pain can be due to an affliction of the underlying structures such as the bones, joints, tendons, connective tissues or nerves. Certain common causes of hand pain include:
- Carpel tunnel syndrome
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Sprain
- Tendonitis
- Ganglion cyst
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Raynaud’s disease
- Injury or trauma
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Proper medical history and appropriate clinical examination can guide towards the probable diagnosis. Certain blood investigations and radiological tests can provide a confirmatory diagnosis. These investigations include:
- Blood investigations:
- Complete blood count (CBC) with erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- C-reactive proteins
- Rheumatoid arthritis factor
- Vitamin D3 levels
- Uric acid levels
- X-ray of the wrist of the affected hand
- MRI scan of the wrist of affected hand to check for entrapment of the nerve
Treatment modalities for hand pain:
The curative treatment of hand pain is dependent on the cause of the pain, yet certain medications along with physical therapy can help in reducing this pain. These treatment options include:
- Medications – Oral analgesic (painkiller) medicines like paracetamol, aceclofenac, and ibuprofen can be used to ease the pain
- Ice packs – The use of ice or ice packs on the hand can help ease the pain
- Physical therapy – Appropriate physical therapy can offer good pain relief for hand pain
- Therapeutic ultrasound can help in reducing the neurogenic or tingling pain

 Doctors for Hand Pain
Doctors for Hand Pain