Summary
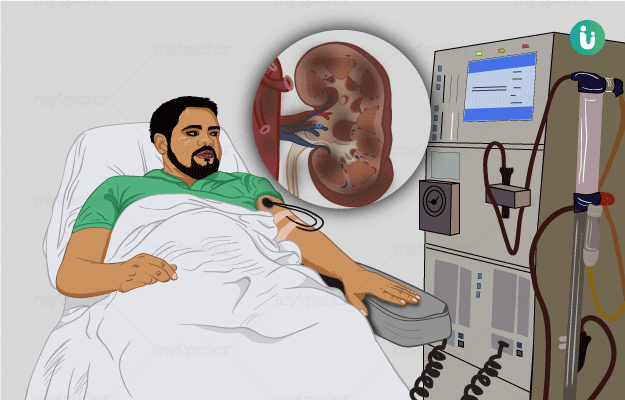
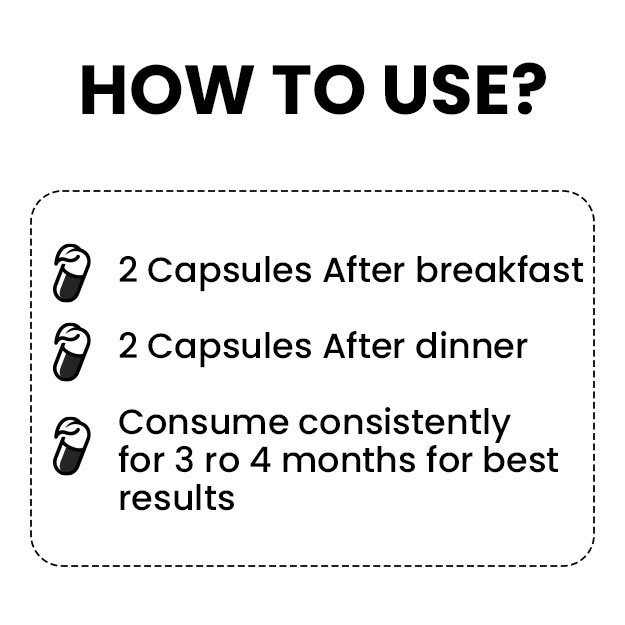
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) (chronic renal disease) is a kidney disease where there is a gradual loss of kidney function. It means that with the progression of the disease, the kidneys gradually are not able to filter blood, the way they normally do. The two most common causes of CKD are diabetes and high blood pressure. In the early stages, kidney disease usually does not show any significant symptoms. Therefore, it is usually diagnosed during routine health check-up through certain blood and urine tests. However, if kidney function worsens despite treatment, or if CKD is not diagnosed in the early stage, then a person may experience symptoms like ankle swelling, blood in urine, muscle cramps increased frequency of urination and breathlessness on little exertion. Treatment of CKD depends on the cause. Along with medications, lifestyle changes play a major role in managing CKD. If kidney function keeps on worsening then one may eventually suffer from end-stage renal disease (ESRD/renal failure/kidney failure), which may require dialysis or a kidney transplant. Kidney failure has been reported in about 1 in 50 people with CKD. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and eventually, kidney failure.

 Doctors for Chronic Kidney Disease
Doctors for Chronic Kidney Disease  OTC Medicines for Chronic Kidney Disease
OTC Medicines for Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease articles
Chronic Kidney Disease articles News for Chronic Kidney Disease
News for Chronic Kidney Disease
 Diet for Chronic Kidney Disease
Diet for Chronic Kidney Disease
 Homeopathic Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease
Homeopathic Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease











 Dt. Akanksha Mishra
Dt. Akanksha Mishra

 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria