Summary
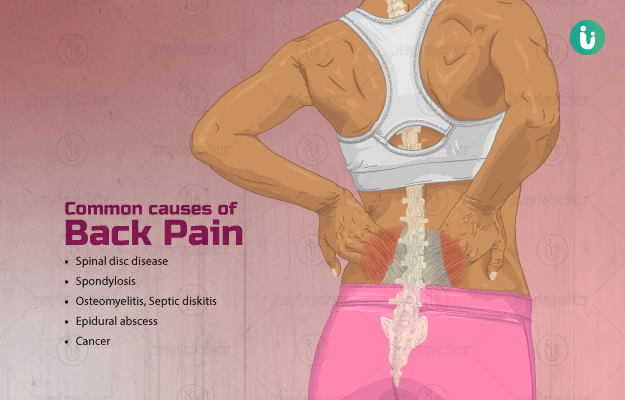
Back pain is one of the most common health problems responsible for frequent doctor visits. It is also the most common reason for absence at work. Back pain can be acute (lasting for a few days or weeks) or chronic (lasting for 3 months and more). Depending on its location, back pain can be dull or sharp, shooting and intermittent, or continuous. Immediate medical attention is required if the pain is associated with tingling and/or numbness in the legs or groins, stiffness with restricted movements or loss of bladder or bowel control. The common causes of low back pain include muscle spasm, injury, slipped or herniated intervertebral disc, spine fracture, sciatica or nerve root compression, arthritis due to aging, osteoporosis, autoimmune disorder (ankylosing spondylitis), spinal stenosis, spine deformities and, cancer. Occasionally, mental stress is also known to cause low back pain, which is frequently neglected. Low back pain sometimes appears as referred pain with the source of pain in different organs, such as the kidneys (example: renal calculus, tumour.), uterus (example: fibroid, menstrual pain and, pregnancy). Acute back pain without any underlying medical problem usually gets better with rest and medication. Acute pain with sudden difficulty in movement, especially after a fracture or slipped intervertebral disc, requires emergency surgery, followed by conservative treatment. Chronic back pain may require long-term management which includes medication, physiotherapy and, specific exercises.

 Doctors for Back Pain
Doctors for Back Pain  OTC Medicines for Back Pain
OTC Medicines for Back Pain
 Lab tests for Back Pain
Lab tests for Back Pain Back Pain articles
Back Pain articles
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Back Pain
Ayurvedic Treatment of Back Pain
 Diet for Back Pain
Diet for Back Pain
 Home Remedies for Back Pain
Home Remedies for Back Pain
 Homeopathic Treatment of Back Pain
Homeopathic Treatment of Back Pain
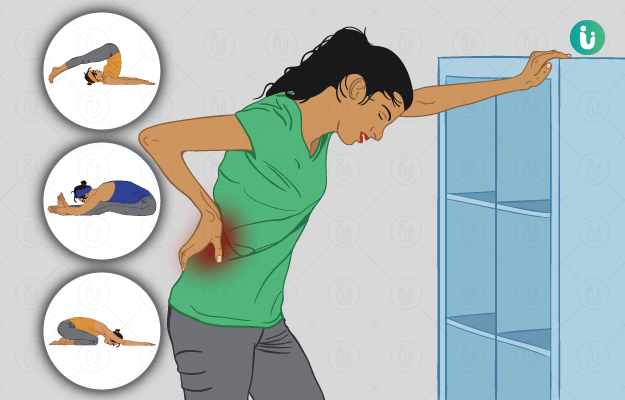
 Yoga for Back Pain
Yoga for Back Pain














 Editorial Team
Editorial Team




 Dt. Akanksha Mishra
Dt. Akanksha Mishra











