Asthma is a breathing disorder that results from narrowing of air passages (bronchi) in the lungs. It is a long-term health condition and can be genetically transmitted. In this disease, the airways are more sensitive to various triggers such as pollen, mould, cockroach droppings, dust mites, and cat or dog fur as well as to infections, and irritants (pollution, different chemicals, perfumes or paints with strong odour, tobacco, weather change, exercise, medicines containing aspirin, artificial preservatives). The muscles in and around the air passages constrict after exposure to the allergic stimulants (allergen) leading to symptoms such as breathlessness, cough, a sensation of tightness in the chest, and wheezing (whistling sound from the chest heard while breathing).
Asthma is common in children who are allergic to indoor allergens (dust in beddings, carpets, pollen, pets), which results in frequent episodes of illnesses and absence from school during childhood. Since there is no cure for asthma, the treatment aims at providing immediate relief during acute attacks and at reducing the frequency of acute attacks. Inhaled steroids, bronchodilators (medicines that relax the muscles and open the air passages), and anti-inflammatory medications are commonly prescribed in the management of asthma. Additionally, self-care, such as knowledge about your triggers and their avoidance; keeping an action plan ready for medications; and breathing exercises significantly help in fighting asthma.

 Doctors for Asthma
Doctors for Asthma  OTC Medicines for Asthma
OTC Medicines for Asthma
 Asthma FAQs
Asthma FAQs Asthma articles
Asthma articles News for Asthma
News for Asthma
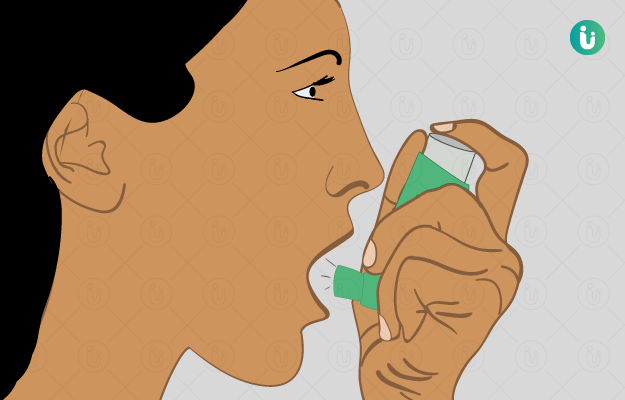
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Asthma
Ayurvedic Treatment of Asthma
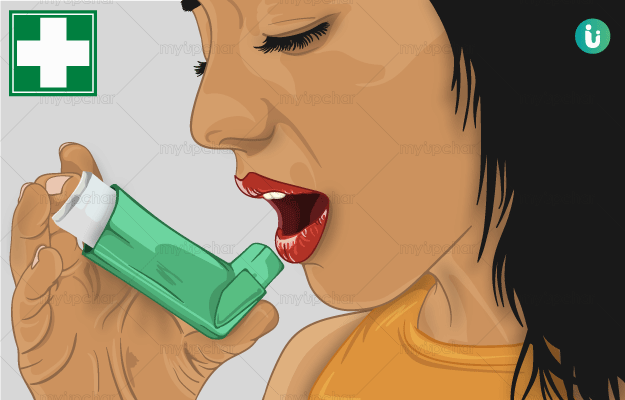
 First Aid for Asthma
First Aid for Asthma
 Homeopathic Treatment of Asthma
Homeopathic Treatment of Asthma
 Yoga for Asthma
Yoga for Asthma




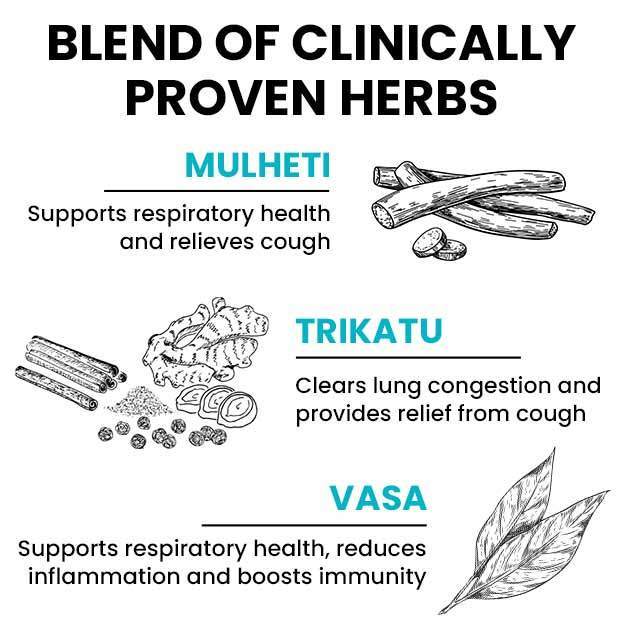

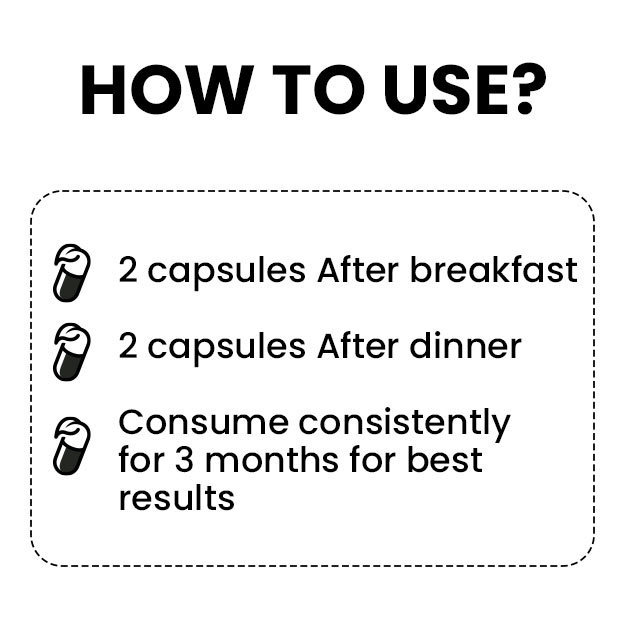




























 Editorial Team
Editorial Team




 Dr. Srishti Gupta
Dr. Srishti Gupta












