What is Anorexia Nervosa?
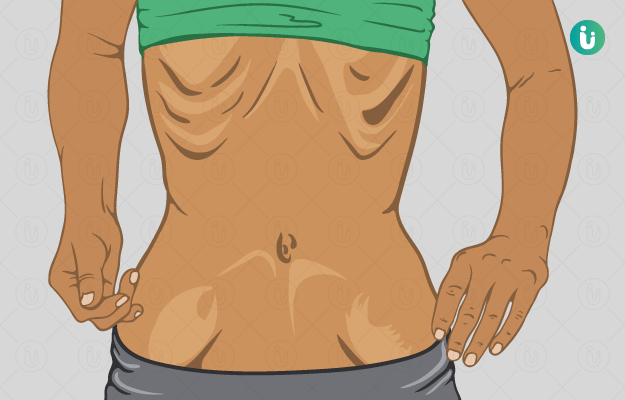
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder as well as a mental illness wherein one’s desire to lose weight leads to inappropriately low body weight. The patient is observed to have distorted ideas of a healthy body and works hard in order to lose weight. Though anorexia nervosa generally begins during adolescence, it is also observed amongst younger children and adults.
What are the main signs and symptoms of Anorexia Nervosa?
- Eating behaviour symptoms:
- Extremely restricted diet, in spite of being thin
- Habitual avoidance of meals with irrational excuses
- Obsession with food and calories while eating very little
- Often pretending to have meals or resorting to lying about eating food
- Appearance and body shape symptoms:
- Sudden, drastic weight loss
- A delusion of being overweight
- Extreme image consciousness to the point of being obsessive
- Constantly self-critical of body and appearance
If you are tired of dieting and exercising and are not able to lose weight, then use myUpchar Ayurveda Medarodh Fat Burner Capsule, it has no side effects, order it today and avail the benefits.
- Symptoms of purging:
- Over-exercising
- Forceful vomiting after eating
- Use of pills (e.g., laxatives) in order to lose weight
- Warning signs and symptoms to watch out for: depression, anxiety, brittle bones and nails, severe loss of hair, frequent fainting.
What are the main causes of Anorexia Nervosa?
Anorexia does not have a single cause, but is a multifactorial disorder.
- Common contributing factors:
- Perfectionism, obsessive and competitive family traits
- Family conflicts
- Academic pressures
- History of eating disorders among family members
- Precipitating factors:
- Abusive childhood
- The onset of puberty or adolescence
How is Anorexia Nervosa diagnosed and treated?
- Criteria for diagnosis:
- The individual does not maintain body weight at or above the minimally normal weight for a particular age and height
- Extreme, unrealistic fear of gaining weight in spite of being underweight
- A distorted idea of one’s appearance in relation to body weight and shape
- In females who have had the onset of menstruation, a minimum of 3 months of no menstruation
- Treatment:
- Hospital admission involving refeeding in order to achieve weight gain is a measure taken for early intervention. This is preferable for young children and teenagers.
- A second approach involves dietary expert advice along with psychotherapy. Here, the family members take responsibility for re-feeding. The results are achieved much slower with this method, but weight gain is more likely to be maintained.
- Psychotherapy for anorexia involves long-term, complex treatments including cognitive and behavioural therapy with an emphasis on cognitive restructuring and added supportive therapy. Supportive therapy is essential in maintaining a healthy therapeutic relationship, whereby the factors leading to anorexia nervosa may be examined and addressed.

 Doctors for Anorexia Nervosa
Doctors for Anorexia Nervosa  OTC Medicines for Anorexia Nervosa
OTC Medicines for Anorexia Nervosa