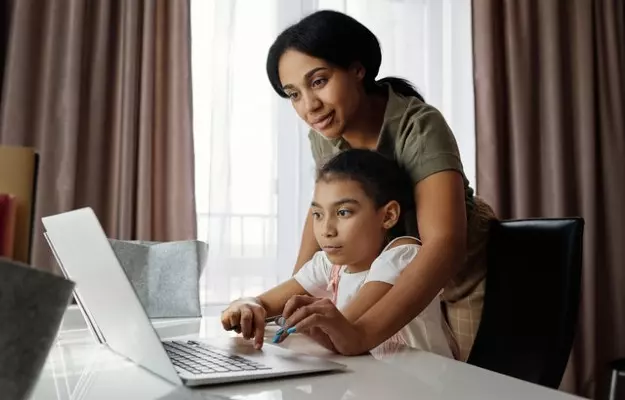
Over eight lakh children worldwide have dangerous levels of lead in their blood, and up to half of these children live in South Asia, according to the latest data by the Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation, US. UNICEF, along with non-governmental agency Pure Earth, released this data on 30 July 2020 in their report titled “The Toxic Truth: Children’s exposure to lead pollution undermines a generation of potential”.
While lead poisoning may happen to anyone of any age, children are particularly vulnerable to it at different stages of their development. For example, foetuses can absorb lead through the expecting mom’s blood. Children also absorb roughly 50% of the lead they ingest with food or water, compared with 10% in grown-ups. Children also tend to put things in their mouths as they explore their surroundings—if they happen to eat dirt or paint with high quantities of lead in them, this can affect their overall development.
Lead has many negative effects on children’s health. Early exposure to lead may lead to immune dysfunction, dementia and other health problems later in life. Indeed, experts have even linked childhood exposure to lead to higher levels of aggression in youths 15 years down the line.
According to the World Health Organization’s 2010 report on “Childhood Lead Poisoning”, “Exposure to lead early in life can re-programme genes, which can lead to altered gene expression and an associated increased risk of disease later in life. Early exposure to lead can also reduce an individual’s capacity to successfully weather other neurological insults later in life.” Neurological insults refer to a physical or mental injury to the central nervous system, including the brain.
Although lead tends to accumulate in the body over the years, early exposure to lead can be particularly dangerous in the short term as well as the long term. Read on to know about the health effects of lead poisoning in children, symptoms of lead poisoning in children, causes of lead toxicity in babies and children, diagnosis of paediatric lead poisoning and treatment of lead poisoning in children.