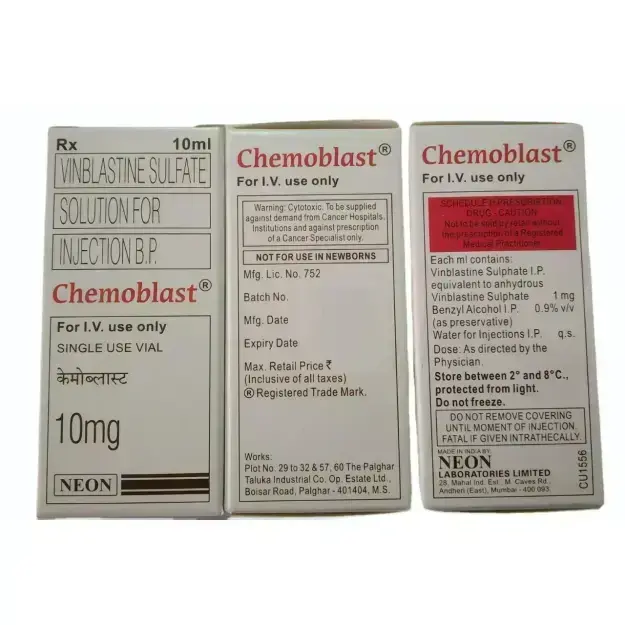
Chemoblast is consists of Vinblastine, is a chemotherapy medication derived from the periwinkle plant (Catharanthus roseus). It belongs to the vinca alkaloid class of drugs and is primarily used for treating various cancers, including Hodgkin’s lymphoma, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, breast cancer, testicular cancer, and Kaposi’s sarcoma. Vinblastine works by inhibiting microtubule formation, preventing cancer cells from dividing and proliferating. Vinblastine remains a cornerstone in cancer chemotherapy, particularly for Hodgkin’s lymphoma, testicular cancer, and Kaposi’s sarcoma. Its role in combination regimens has significantly improved survival rates for many patients. However, its myelosuppressive effects necessitate careful monitoring. With ongoing advancements in drug delivery and combination therapies, vinblastine’s effectiveness may continue to improve in the coming years.
Mechanism of Action
Vinblastine is a mitotic inhibitor that functions by binding to tubulin, a protein essential for microtubule formation. Microtubules play a crucial role in cell division, and by preventing their assembly, vinblastine halts mitosis in the metaphase, leading to cancer cell death.
Key Mechanisms
-
Microtubule Disruption: Prevents mitotic spindle formation, blocking cell division.
-
Apoptosis Induction: Leads to programmed cell death in rapidly dividing cancer cells.
-
Reduced Angiogenesis: Inhibits the formation of new blood vessels that feed tumors.
Indications & Uses
-
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma – Used in combination chemotherapy regimens like ABVD (Adriamycin, Bleomycin, Vinblastine, and Dacarbazine).
-
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma – Effective in slowing disease progression.
-
Testicular Cancer – Part of BEP (Bleomycin, Etoposide, and Platinum-based therapy).
-
Breast Cancer – Used in advanced-stage or recurrent cases.
-
Kaposi’s Sarcoma – Treats aggressive cases in immunocompromised patients (e.g., HIV/AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma).
-
Bladder Cancer & Lung Cancer – Investigated for efficacy in metastatic settings.
Dosage & Administration
Typical Dosages:
-
Lymphomas: 6 mg/m² IV every 7-14 days.
-
Testicular Cancer: 3 mg/m² IV weekly.
-
Breast Cancer & Kaposi’s Sarcoma: Dosage varies depending on combination regimens.
-
Pediatric Dosing: Adjusted based on body surface area (BSA) and tolerance.
Efficacy & Clinical Trials
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (ABVD Trial):
Testicular Cancer (BEP Regimen Studies):
Kaposi’s Sarcoma (AIDS-Related Trials):
Side Effects & Toxicity
Common Side Effects:
-
Bone Marrow Suppression: Leads to leukopenia (low white blood cell count), increasing infection risk.
-
Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, constipation.
-
Neuropathy: Mild to moderate peripheral neuropathy.
-
Alopecia: Temporary hair loss.
-
Fatigue & Weakness.
Serious Side Effects:
-
Severe Myelosuppression: Can lead to life-threatening infections.
-
Neurotoxicity: Less common than vincristine but can still occur.
-
Extravasation Risk: Severe local tissue necrosis if it leaks outside the vein.
Contraindications & Precautions
Contraindications:
-
Severe leukopenia (low WBC count).
-
Hypersensitivity to vinca alkaloids.
-
Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Precautions:
-
Renal & Hepatic Impairment: Dose adjustments required.
-
Neuropathy Risk: Monitor for tingling or numbness.
-
Vaccinations: Avoid live vaccines during therapy.
Drug Interactions
-
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (e.g., Ketoconazole, Erythromycin): Increase vinblastine levels, enhancing toxicity.
-
CYP3A4 Inducers (e.g., Rifampin, Carbamazepine): Reduce vinblastine efficacy.
-
Other Chemotherapy Agents: Increased bone marrow suppression when combined with cisplatin or doxorubicin.
-
Antifungal Medications (Itraconazole, Fluconazole): May exacerbate side effects.
Storage & Handling
-
Store at 2-8°C (Refrigerated).
-
Protect from light to prevent degradation.
-
Use within prescribed time after dilution.
-
Safe disposal required due to cytotoxic nature.
X