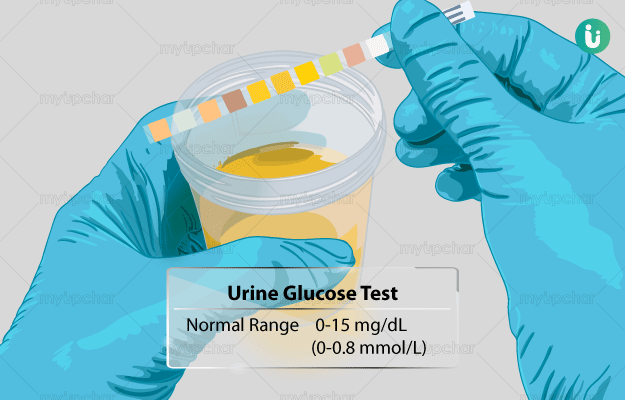
What is Urine Glucose Test?
A urine glucose test is a screening test for diabetes that is done to check for the presence of excess glucose in the urine of an individual.
If you want to know what is the treatment of diabetes, then definitely click on this link.
Glucose is a simple sugar that makes the primary energy source of our body. It is made by the breakdown of carbohydrates by our digestive system and is taken up by body cells with the help of a hormone called insulin. Excess blood glucose, as in the case of diabetes, is eliminated through urine. Thus, a urine glucose test indirectly helps to determine if the blood glucose levels are too high. This test is usually suggested in cases where a blood glucose test is not feasible such as in people who have small veins that can't be easily detected for blood withdrawal or patients who have multiple needle punctures due to insulin uptake or repeated tests. Abnormal results in urine glucose test, however, do not confirm the diagnosis; a blood glucose test is done for that purpose.
(Read More - Diabetic retinopathy)