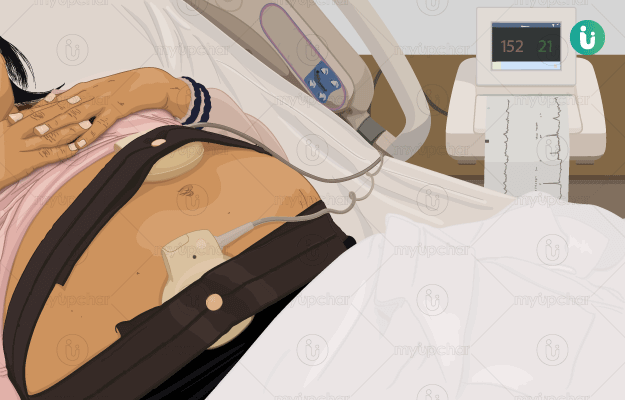
What is Non-Stress test (NST)?
A non-stress test (NST) is usually performed during the last trimester of pregnancy to measure the heart rate (number of heartbeats per minute), baby movement and reactivity of the heart rate to the movement. In a majority of cases, heart rate of the foetus increases with its movement. It can be done any time after 26 to 28 weeks depending upon the purpose for which it is performed.
The name non-stress comes from the fact that no external stress is placed on the baby during the test.