What is a KOH Fungal Smear test?
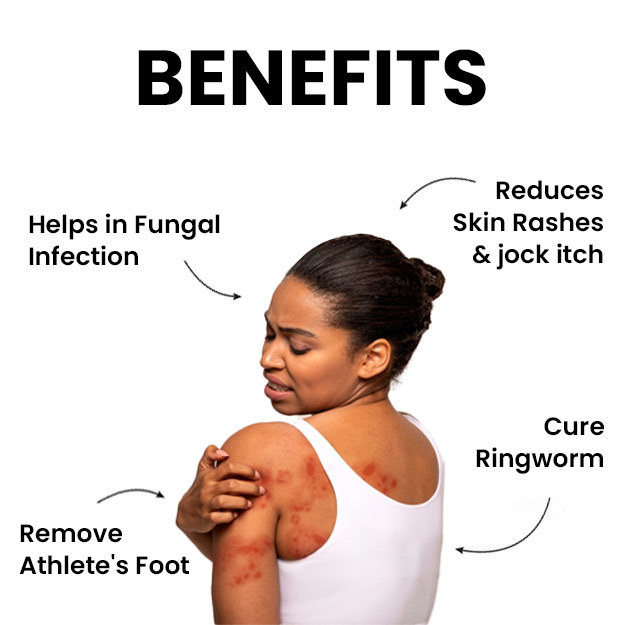
Fungi are tiny organisms found everywhere in the environment. They grow anywhere from walls, food, clothes and paper. Fungi are even present (as spores) in air. There are millions of fungal species in the world; however, only a few can cause infections in humans. Fungal infections are mostly superficial. These include:
- Skin infection (ringworm or tinea)
- Nail infection (onychomycosis)
- Infection in the mouth (thrush)
- Infection in the vagina (vaginal candidiasis or yeast infection)
Fungi can also grow on hair and scalp. Regardless of type, all fungal infections can easily spread from one person to another.
In rare cases, fungi may cause serious infections, involving the lungs, bloodstream, brain or other organs in the body. Though serious fungal infections are more likely in people with a weak immune system.
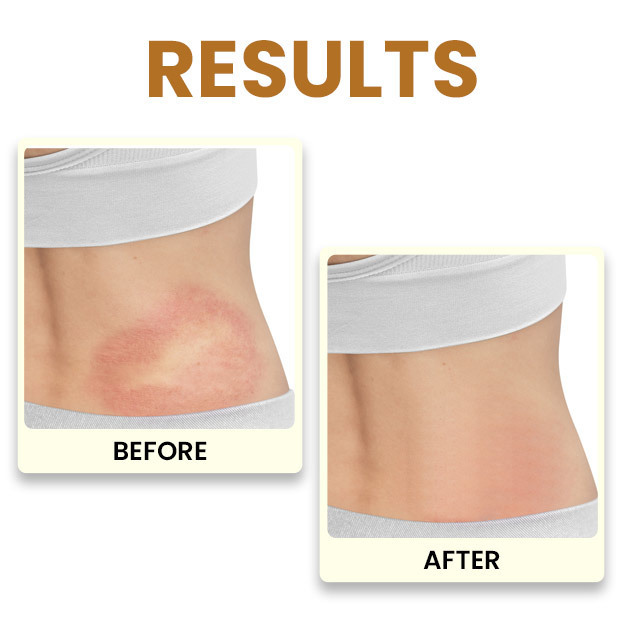
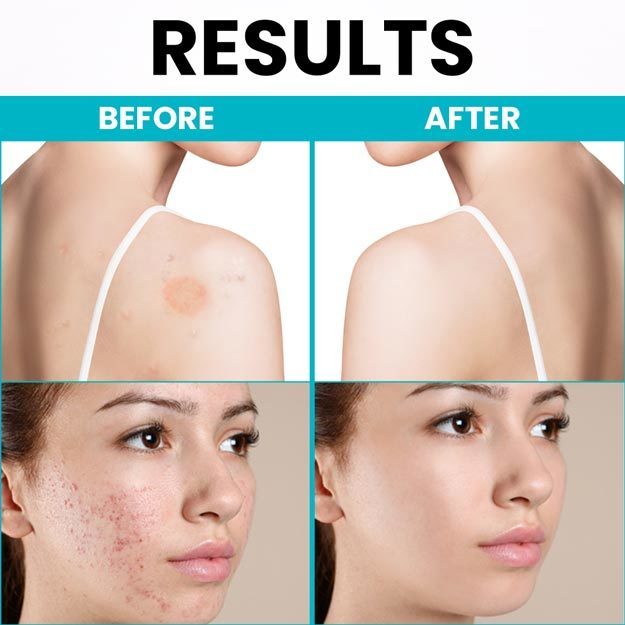
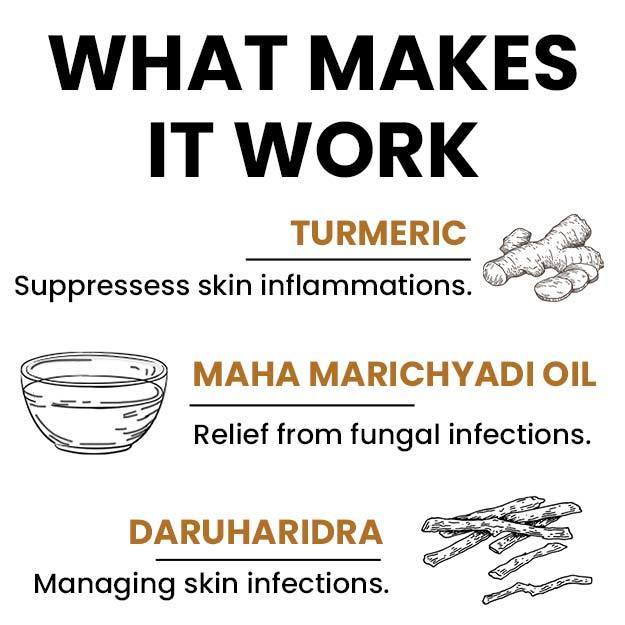
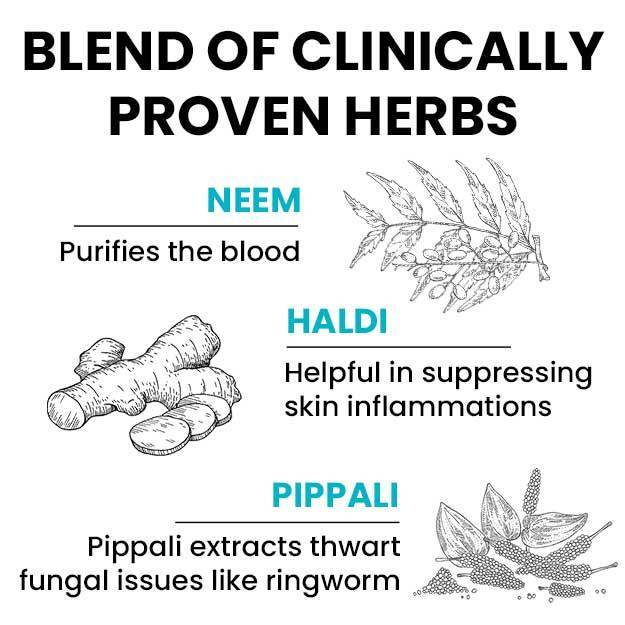
The KOH test is a simple test performed to diagnose a fungal infection. KOH stands for potassium hydroxide. When mixed in a tissue sample (skin, hair or nails), KOH dissolves the non-fungal cells, leaving only the fungal cells behind. The sample is then directly examined under a microscope to detect and identify fungal elements to determine the right treatment.