What is an Iron test?
Iron tests refer to a group of tests that measure the level of iron reserves in body. Iron is essential for metabolic functions. An adult has an average of 3-5 grams of iron, of which two-thirds are present in haemoglobin. Iron tests detect both low and excess levels of iron in body.
The different types of iron tests are as follows:
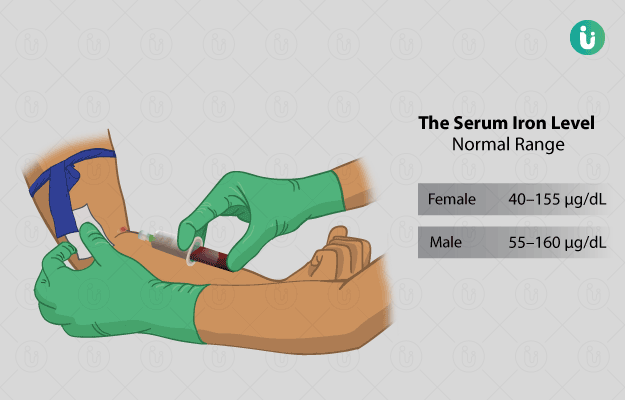
- Serum iron: To determine the level of iron in serum.
- Transferrin: Iron is transported in the body by transferrin. Approximately, 33% of transferrin is normally saturated with iron.
- Total iron binding capacity/serum iron and transferrin: Total iron binding capacity (TIBC) is a measure of the total amount of iron combined with proteins in blood.
- Hypochromic cells in peripheral blood: The percentage of hypochromic cells (paler than normal RBCs) in a peripheral blood smear is determined.
- Serum ferritin: Serum ferritin levels indicate the amount of iron in the whole body.
Low levels of iron commonly lead to a condition called iron-deficiency anaemia. If the levels of iron are higher than normal, it is deposited in different parts of the body and leads to organ dysfunction. This condition may be caused by excess iron intake or increased absorption of iron.