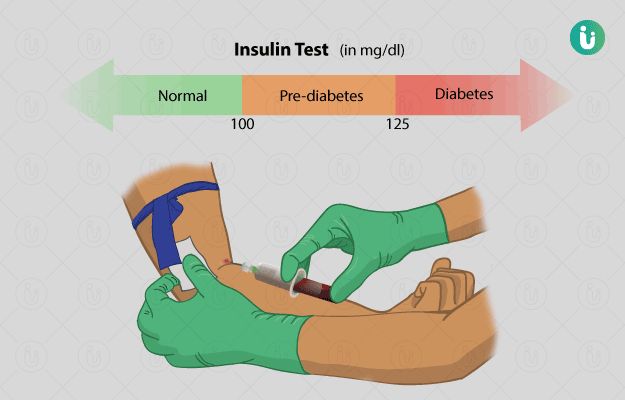
What is an Insulin test?
Insulin is a vital hormone secreted by the beta cells of pancreas. It regulates glucose metabolism by assisting the transport of glucose from blood to tissue cells. Glucose is an important energy source in the body. Raised blood glucose levels after a meal stimulate beta cells to secrete insulin to transport excess sugar out of the bloodstream. Insulin thus plays an important role in regulating glucose levels inbody.
Please click on the given link and know about diabetes treatment.
In certain disorders, beta cells cannot secrete enough insulin, causing an increased blood glucose state called hyperglycaemia. In other scenarios, insulin secretion in body may be normal, but body cells become resistant to its effects. This condition is known as ‘insulin resistance’. In Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, reduced insulin secretion is the cause of hyperglycaemia, whereas Type 2 diabetes mellitus usually results due to insulin resistance. Occasionally, increased levels of insulin are observed in the body due to hyperinsulinemia. It may lead to various metabolic imbalances.
An insulin test is a blood test used to detect the levels of insulin in blood. Insulin levels in blood may be indicative of the probable cause of metabolic derangements occurring in the body.
(Read More - Stages of type 1 diabetes)