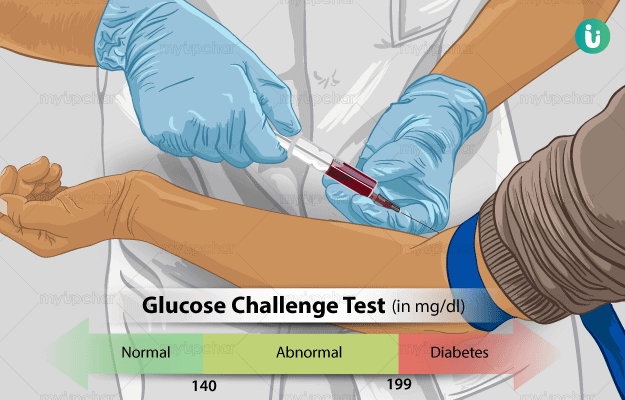
What is a Glucose Challenge test (GCT)?
A glucose challenge test (GCT) is used to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes in a wide range of population, including the elderly and youngsters, overweight individuals and individuals with or without a family history of diabetes. It is also recommended for the diagnosis of gestational diabetes in pregnant women, which occurs only during pregnancy and affects both the mother and the baby. GCT determines how glucose is processed in body and a glucose tolerance test is needed to confirm the presence of diabetes in women with abnormal results on GCT.
Click on the link given here, to know in detail about diabetes treatment.
GCT is considered a standard test to be performed during the early phase of the third trimester of pregnancy. It is generally recommended during the 24th to 28th week of pregnancy. Timely diagnosis and appropriate management of this condition can help prevent pregnancy complications.
(Read More - Diabetic Ketoacidosis treatment)