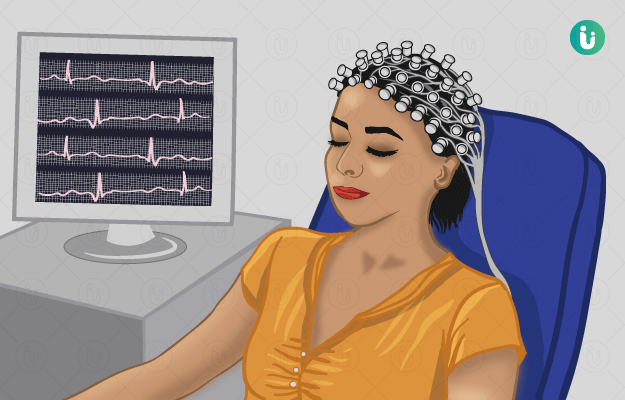
What is an Electroencephalogram?
An electroencephalogram or EEG is a reading of a test that is done to record the electrical activity of the brain. Electrical signals are picked up and amplified by special electrodes attached to the scalp. These signals appear as a graph on a computer, which is then printed on a paper. The graph is then interpreted by a healthcare provider or a specialist to identify any unusual activity. This procedure is conducted by highly trained clinical neurophysiologists at a hospital and typically lasts for 45-120 minutes. Results are usually deciphered on the basis of waveforms, energy and responses to stimuli such as flashing lights.