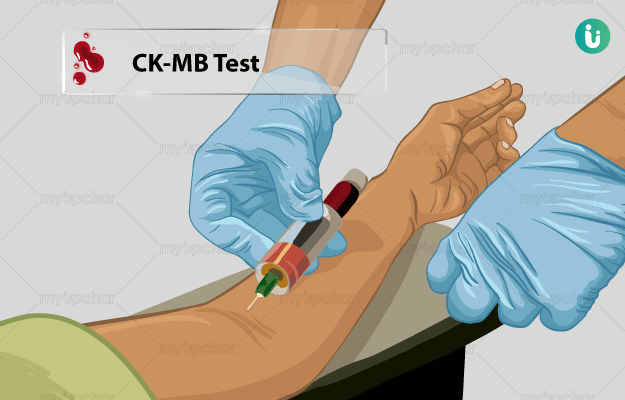
What is a Creatine Kinase Isoenzyme MB (CK-MB) test?
Creatine kinase also referred to as creatine phosphokinase (CPK), is an enzyme found predominantly in the heart and skeletal muscles and in small quantities in the brain. During an injury, stress or muscle damage, it is secreted into the bloodstream.
A CK-MB test is usually suggested to diagnose acute myocardial infarction or a heart attack. CK-MB exists in two forms. CK-MB 2 is released by cardiac cells and is converted to CK-MB 1 in blood. A prompt assay, within 6 hours of the onset of cardiac symptoms, helps in the correct diagnosis of myocardial infarction.
Test results can be confirmed by clinical diagnosis and evaluation of other cardiac biomarkers.