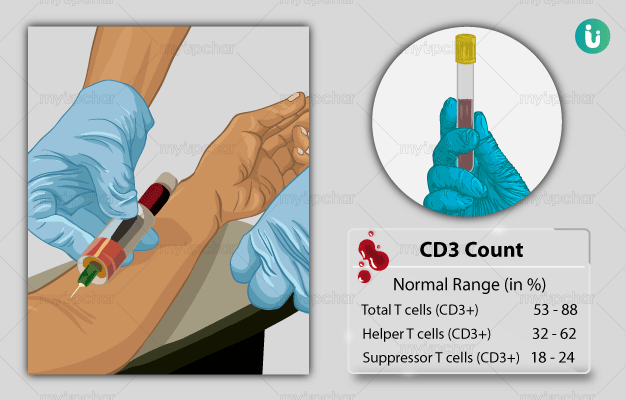
What is a CD3 Count test?
CD3 or cluster differentiation 3 is a bunch of different fractions or subunits of protein (gamma or γ, delta or δ, epsilon or ε and zeta or ζ) that are attached to the surface of T cells. T cells or T lymphocyte cells are a type of white blood cells which play an important role in regulating the immune response. There are different types of T cells such as T helper cells, cytotoxic or suppressor T cells and so on. All these types of mature T cells have special molecules known as T-cell receptors (TCRs) on their surfaces with CD3 proteins as co-receptors located close to TCRs. Due to their proximity with TCRs CD3 surface markers are also known as pan-T-cell markers.
T cell receptors identify foreign substances and send a signal to the CD3 markers about their presence. The latter then convert the signal and initiates a complex series of chemical reactions that trigger other immune system cells to destroy the foreign body.
Since they are so closely linked to T cells, a CD3 test is used to detect abnormalities in the values or amount of T cells in conditions arising from weak immunity such as HIV. They also help diagnose immune system disorders caused due to increased T cells such as in cancer, and organ transplant.