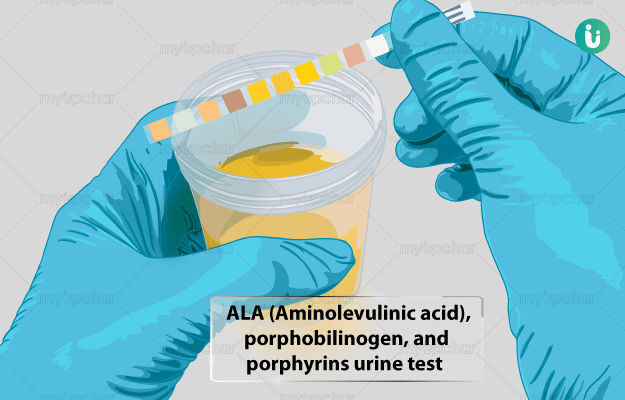
What is ALA (Aminolevulinic acid), porphobilinogen, porphyrin urine test?
ALA, porphobilinogen and porphyrias are compounds that are formed as intermediates in the production of haem - an iron-containing pigment present in red blood cells (RBCs).
Aminolevulinic acid and porphobilinogen are the initial products produced during the process. These are then converted to porphyrins in the presence of different enzymes. However, it takes eight different enzymes to complete the process.
If there is a defect or deficiency of any of the eight enzymes, it interferes with the whole process and leads to accumulation of intermediate porphyrins, such as uroporphyrins and coproporphyrins, in body fluids and tissues.
Some amount of porphyrins are always present in blood and urine. However, if porphyrins build-up in the body, they lead to a condition called porphyria. Porphyria can produce harmful effects on the nervous system and skin.
This test checks the levels of intermediate porphyrins such as uroporphyrin and coproporphyrin in the urine. It is used in the diagnosis and monitoring of porphyrias. E.g., high level of a porphyrin precursor called porphobilinogen, PBG, (over 6mg per day) in the urine indicates the presence of acute intermittent porphyria, variegate porphyria or hereditary coproporphyria.
The test may also be used for the diagnosis of lead poisoning and liver damage. ALA levels tend to remain high in the urine of individuals with lead poisoning. Decreased ALA level may be indicative of liver damage.
There are several types of porphyrias, depending on the enzyme defect and the porphyrin that accumulates in the body.
(Read more: ALA (Aminolevulinic acid), porphobilinogen, porphyrin blood test)