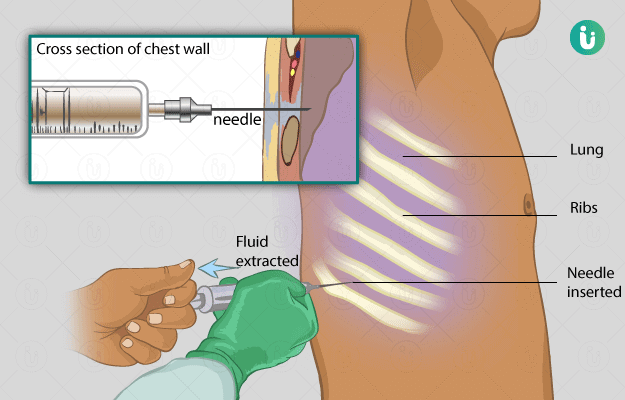
What is an Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) test?
An ADA test is a biochemical evaluation of the levels of enzyme ADA in body fluids, such as serum, sputum, pleural effusions, synovial effusions and ascites. This test is commonly performed to aid the diagnosis of tuberculosis along with the other conventional tests. Tuberculosis is endemic to India with the equal prevalence of pulmonary, and extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
ADA enzyme is an important biomarker for the early diagnosis of tuberculosis. It is responsible for the conversion of adenosine to inosine during purine metabolism. Lower levels of adenosine deaminase may prevent the formation of T and B lymphocyte cells resulting in reduced immunity and increased susceptibility to bacterial and viral infections. Deficiency of ADA causes severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome, and the affected patients suffer from multiple infections.
Tubercular effusions occur as an immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis; hence, they have elevated levels of ADA. There are two isozymes of ADA, viz ADA1 and ADA2, which are responsible for the ADA activity. An ADA kit is available in most laboratories to determine the concentration of ADA in the fluid under evaluation.