| Week |
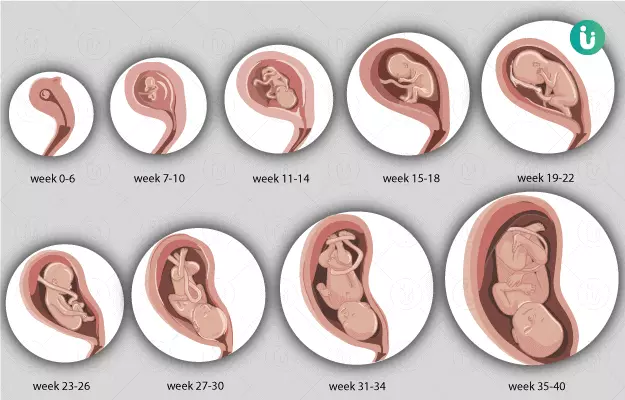
Baby growth and development |
| Week 1 |
This is actually your menstrual week. The duration of pregnancy is calculated from the first day of your previous cycle. So, fertilisation has not yet occurred. |
| Week 2 |
Ovulation occurs during this week, which may be accompanied by mild bleeding or spotting. This releases your egg and makes it available for fertilisation by the male gamete. |
| Week 3 |
Fertilisation occurs now as the male and female gametes unite to form a zygote at the end of fallopian tube. 30 hours after this, it divides to form a two-celled structure. 3 days later, the zygote forms a 16-celled structure, called a morula. |
| Week 4 |
The morula then begins to move from the end of the fallopian tube to the uterus, where it gets implanted. It buries itself into the thick lining of the uterine wall (endometrium) and is now called a blastocyst.
The cells then begin to divide rapidly and your baby is about the size of a grain of rice.
|
| Week 5 |
The neural tube evolves, which will later develop the brain and the spinal cord.
The heart and its circulation begin to form and you miss your period and run a positive pregnancy test due to the hormones released by the developing baby.
|
| Week 6 |
The baby is now called an embryo and is 3 mm in length. The head and the upper part of the body develop and the heart acquires a tubular shape.
At this stage, the embryo curls up in the uterus and acquires a tadpole-like form.
Eyes may begin to form and buds for the development of limbs appear.
Neural tube slowly starts to develop the brain and the spinal cord.
|
| Week 7 |
The tubular-shaped heart develops a heartbeat. Amniotic sac and placenta start developing for protection and nutrition respectively.
Slowly, the placenta buries itself into the uterine wall in order to derive nutrition and oxygen.
|
| Week 8 |
The heart differentiates and forms its chambers. The well-formed 4 chambers start to develop their function. The circulation is still derived through the umbilical cord.
Vertebral column begins to develop but comprises of cartilage instead of bone.
Nervous system continues to develop and electrical activity begins.
Fingers of the embryo start to form. At 8 weeks, the head of the embryo is disproportionately large and the forming spinal cord looks like a tail. Embryo is 1.3 cm in length.
|
| Week 9 |
Mouth and tongue start forming along with the development of the eyes.
The muscles of the embryo begin to develop, which assists its movements.
RBCs are being produced.
|
| Week10 |
Marking a transition, the embryo is now called a foetus and loses its tail. The head is still large but it evolves to a more human-like form. Arms, legs, fingers and toes are distinctly visible now along with the formation of eyelids.
Bony cells replace the cartilage. The foetus is 2.5 cm in length.
|
| Week 11 |
Heart begins to differentiate and tooth buds develop inside the gums. |
| Week 12 |
The eyelids are fused and already formed web-like fingers start developing nails. The foetus begins to move about a bit and its heartbeat can be felt by foetal ultrasound. |
| Week 13 |
7 cm in length, the foetus swims around vigorously within the protective sac. |
| Week 14 |
The toes also start developing nails now. Swallowing functions evolve and the kidneys are able to synthesise urine. The foetus is 3.5 inches long and its arms are now in proportion to the body. It begins to develop a sleep-wake routine of its own. |
| Week 15 |
The fingers and toes continue to grow nails. |
| Week 16 |
Sex can be determined by now and the body of the foetus is covered by a protective layer of hair called lanugo. The head starts to become erect and taste buds develop. |
| Week 17 |
The foetus is 5 to 6 inches long and weighs about 4 ounces. |
| Week 18 |
Body and facial features are well formed and evident as nose, lips and ears. Scalp hair is also seen. |
| Week 19 |
The foetus begins to respond to sound stimulus. You may feel the hiccoughs of the baby at times. |
| Week 20 |
Ears are fully functional and can hear the sound from the outside. The genitals can now be distinguished by a scan. The oil glands of the baby develop and secrete sebum. |
| Week 21 |
Baby starts moving around with the first movement being as thumbsucking. This can even be seen on an ultrasound. Baby movements in the form of kicks, flutters and punches may also be felt. |
| Week 22 |
Lower limbs are fully formed and toenails develop completely. |
| Week 23 |
The foetus begins to gain some weight and its skin is red and wrinkled. |
| Week 24 |
Fused eyelids separate to distinct upper and lower eyelids and allow the foetus to shut and open its eyes. The foetus is able to breathe and breathing movements are also present. |
| Week 25 |
Eyebrows and eyelashes are distinctly visible. |
| Week 26 |
The foetus can respond to external sounds and those within the uterus. |
| Week 27 |
An increase in the size of foetus gradually occurs. |
| Week 28 |
The foetus now weighs a kilogram and has a more proportionate body as the body grows to keep up with the size of the head. |
| Week 29 |
The foetus is 14 inches long. |
| Week 30 |
The foetus weighs 2.5 pounds and its lungs continue to develop. |
| Week 31 |
The foetus grows and matures and acquires more fat. |
| Week 32 |
It now weighs 3 to 4 pounds and is covered by a thicker layer of vernix. |
| Week 33 |
The baby is mostly asleep and its movements are more coordinated. It now acquires a heads down position preparing for delivery. |
| Week 34 |
Kicks and movements become stronger and the fingernails reach the end of fingertips. |
| Week 35 |
As the lungs continue to develop, the baby nestles its head between the pelvic bones of the mother. |
| Week 36-38 |
Muscle tone is developed and the foetus can lift its head. It has soft earlobes with limited cartilage. Grasping skills improve and lanugo disappears as the baby gains fat. |
| Week 39-40 |
Testicles descend into the scrotum and vulva develops. The chest becomes prominent and the foetus prepares itself for delivery. |