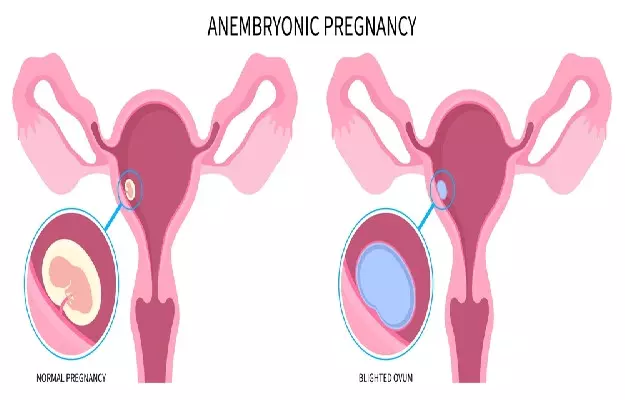
When a fertilized egg implants itself in the uterus but does not form an embryo, it is known as a blighted ovum or anembryonic pregnancy. Most miscarriages occur due to this. The placenta and embryo sac are formed in the stomach, but remain empty. One cannot become a growing child. Even if no embryo forms, the placenta still produces human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). This hormone is necessary for pregnancy. HCG hormone can be found when seen in blood and urine tests, so a blighted ovum may result in a positive pregnancy test, even if an embryo is not forming in the womb.
When a woman becomes pregnant, the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. At about five to six weeks of pregnancy, the embryo should become visible. At this time, the gestational sac – where the embryo develops – is about 18 millimeters wide. Other pregnancy-related symptoms, such as breast pain and nausea, may also occur.
(Read more - Pregnancy diet: What to eat)