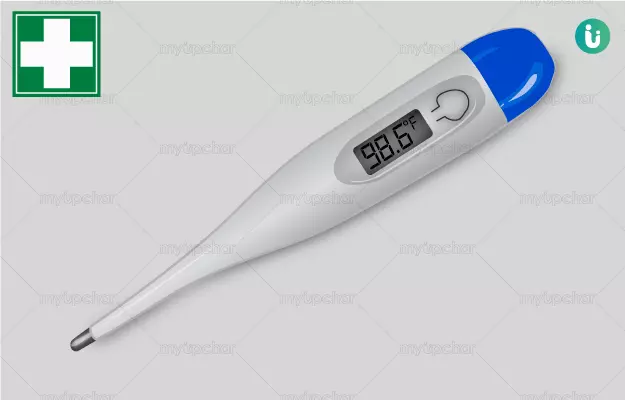
We have all been brought up being told that the average body temperature is 98.6°F or 37.0°C. Every school kid knows this and it is one of the first important things we learn about our health; we know that our temperature is a vital sign and significant deviations are a sign that something is amiss.
The 98.6°F figure has been in use since 1851, when a German doctor named Carl Wunderlich calculated the average of 25,000 people’s temperatures. This was a large sample size and the figure was probably a reasonable estimate for that time. However, a string of new studies have shown that the average temperature of adults may be quite lower-- somewhere between 97.5°F and 97.9°F.
In fact, the term ‘normal temperature’ is also a bit of a misnomer - it is more accurate to think of normal temperatures as a range. Generally speaking, temperatures between 97°F and 99°F are considered normal in adults. However, every person has variations of their own, and temperature also changes during the day. The body is coolest early in the morning and slightly warmer in the evening.
Further, older people have slightly lower average body temperatures, and babies and children have slightly higher average temperatures. Women are also slightly warmer than men, and body temperature also varies slightly by season.
Despite this range and differences across demographics, a body temperature of over 100°F taken by the mouth is considered a fever. A temperature below 95°F is abnormally low and could be a sign of hypothermia. This is a dangerous situation and medical intervention will be required.
The way temperature is measured also matters; armpit readings are 1°F lower on average when compared to mouth readings, and rectal readings are slightly higher than mouth readings.