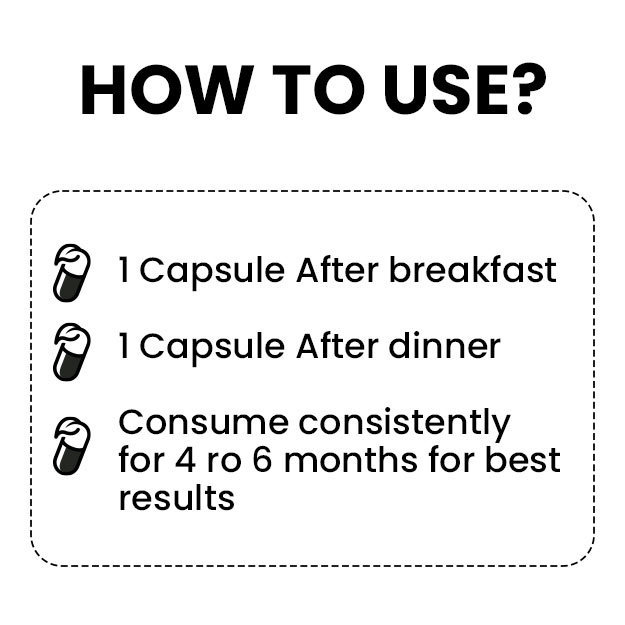
First aid is the immediate emergency care given to an injured or ill person until medical help arrives. In some minor cases, first aid itself could be enough to deal with injuries.
Offer - Urjas Oil for just ₹ 1
X

- हिं - हिंदी
- En - English
- म - मराठी
- తె - తెలుగు
- த - தமிழ்
- বা - বাংলা