Summary
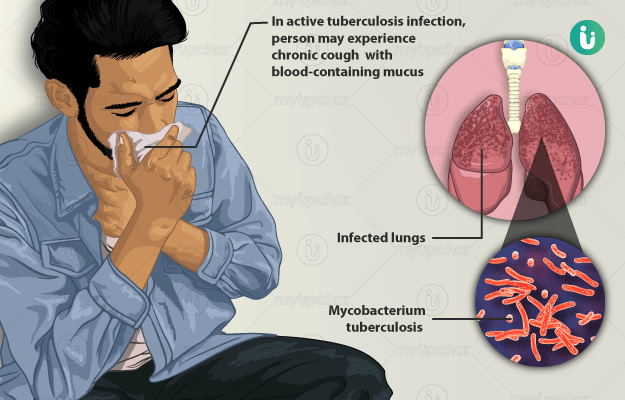
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is one of the major health concerns across the globe, especially in developing countries. It is estimated that one-third of the world’s population has latent tuberculosis. It is a contagious disease and spreads through contact with an infected person. After entering the body, the TB pathogen usually harbours in the lungs. The pathogen adversely affects the lungs causing cough, blood-stained phlegm, fever, and weight loss. Sometimes, it also affects the bones, meninges (brain coverings), kidneys, and intestines. TB is commonly treated with drugs known as Anti Koch drugs and the treatment usually lasts from six months to three years depending upon the type and severity of the disease. If a person receives timely appropriate treatment, then the success of treatment is near to cent per cent. But sometimes, TB may relapse or in extreme cases, cause death.

 Doctors for Tuberculosis
Doctors for Tuberculosis  OTC Medicines for Tuberculosis
OTC Medicines for Tuberculosis
 Lab tests for Tuberculosis
Lab tests for Tuberculosis Tuberculosis articles
Tuberculosis articles News for Tuberculosis
News for Tuberculosis
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Tuberculosis
Ayurvedic Treatment of Tuberculosis
 First Aid for Tuberculosis
First Aid for Tuberculosis
 Homeopathic Treatment of Tuberculosis
Homeopathic Treatment of Tuberculosis
































 Editorial Team
Editorial Team



 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria

 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla











