Summary
A sore throat is a symptom seen in children as well as in adults. It is one of the commonest conditions that doctors treat in outpatient departments. There are over 200 microorganisms including bacteria and viruses that can cause a sore throat. An acute sore throat is more common in children living in areas where the risk of acquiring an infection or re-infection is very high, such as crowded places and places with poor living conditions. One of the most common causes of a sore throat is flu or a common cold. Viral and bacterial infections spread from person to person via air, mostly through nasal or salivary secretions of an infected individual. Crowded places, poor hygiene, unhygienic handling of food, exposure to chemicals, smoke, and irritants may trigger the onset of a sore throat. Besides a difficulty in swallowing, it may be accompanied by other symptoms like fever, rash or a headache.
A detailed medical history is essential to evaluate the exact cause of a sore throat, as it can also occur due to a wide range of illnesses. Most cases of a sore throat resolve without any medications but several individuals may require a course of antibiotics. A sore throat caused by the Streptococcus bacteria needs to be properly treated with antibiotics to prevent further complications. Other causes of a sore throat may need more complex and disease-specific treatment. Complications of a sore throat may be seen in 1% of the cases, irrespective of whether the patient received an immediate or delayed course of antibiotics.

 Doctors for Sore Throat
Doctors for Sore Throat  OTC Medicines for Sore Throat
OTC Medicines for Sore Throat
 Lab tests for Sore Throat
Lab tests for Sore Throat Sore Throat articles
Sore Throat articles
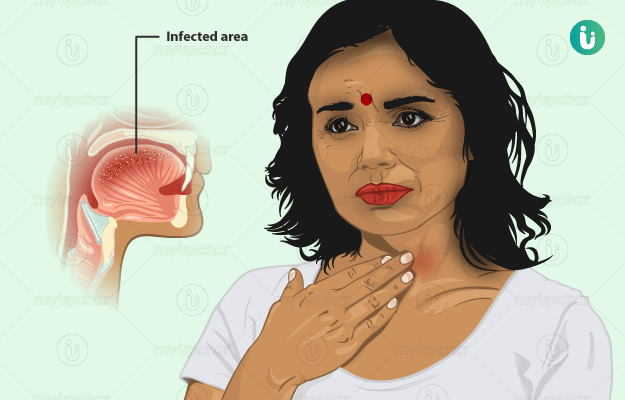
 First Aid for Sore Throat
First Aid for Sore Throat
 Home Remedies for Sore Throat
Home Remedies for Sore Throat
 Homeopathic Treatment of Sore Throat
Homeopathic Treatment of Sore Throat




































 Editorial Team
Editorial Team
 Dr. Ajay Mohan (AIIMS)
Dr. Ajay Mohan (AIIMS)

 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria











