Summary
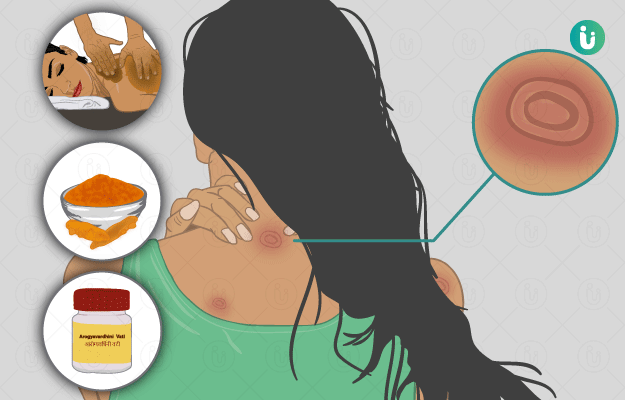
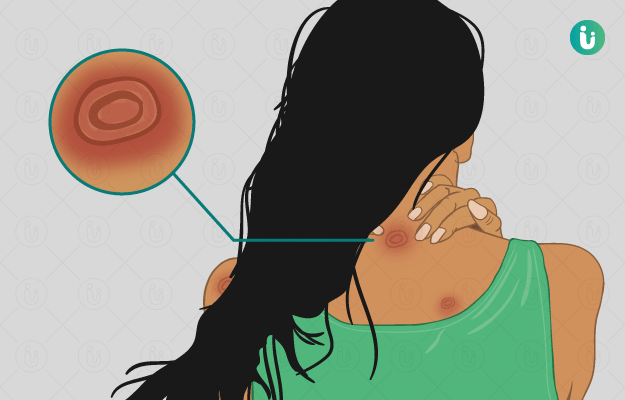
Ringworm is a common skin infection that is seen in both children and adults. A fungus known as dermatophyte causes ringworm. Medically known as tinea, ringworm can affect human beings as well as animals. Ringworm infection occurs on the skin areas that are usually warm and moist, such as the skin folds between the toes, groin region, scalp, fingers among others. Different types of ringworm are named after the skin area that is involved. For example, tinea cruris occurs in the groin, tinea capitis in the scalp, tinea unguium in the toenails, tinea pedis (athlete’s foot) in the feet, and tinea manuum in the hands. Tinea corporis is a general term used for a fungal infection occurring anywhere on the body.
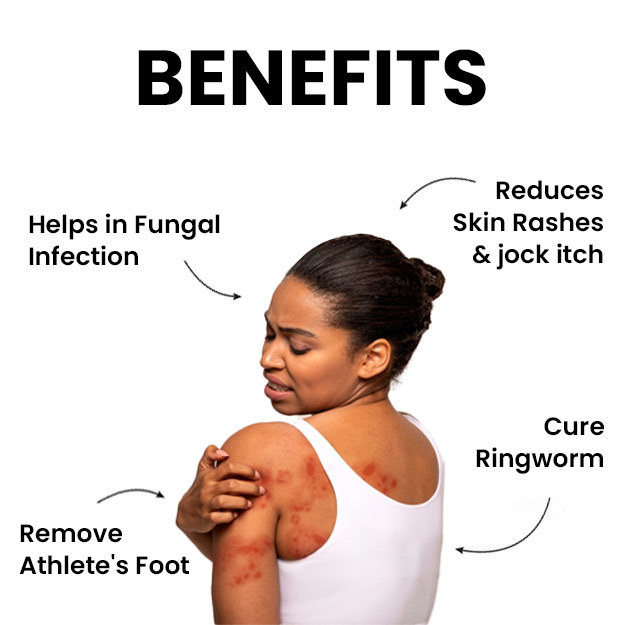
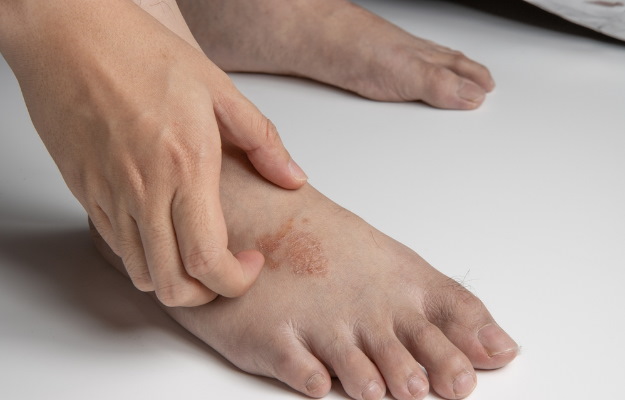
Ringworm appears in the form of a circular ring-like rash with a clear area in the centre. The edges of the ring are raised, red coloured and scaly. In ringworm, there is intense itching in the affected area. The term ‘ringworm’ is given to tinea because of the characteristic circular ring-like appearance of the rash. Ringworm spreads easily from an infected person, animal or pet, and also through soil or surfaces that have fungi. It is also commonly seen in people with weak immunity such as those with HIV, diabetes, and cancer. Doctors diagnose ringworm on the basis of physical and microscopic examination of the infected skin sample. Mild forms of ringworm usually resolve with external application of anti-fungal ointments and lotions. However, oral anti-fungal medicines are also required in severe cases. Additionally, maintaining healthy habits to keep the skin clean and hygienic help in preventing ringworm.

 Doctors for Ringworm
Doctors for Ringworm  OTC Medicines for Ringworm
OTC Medicines for Ringworm
 Ringworm articles
Ringworm articles
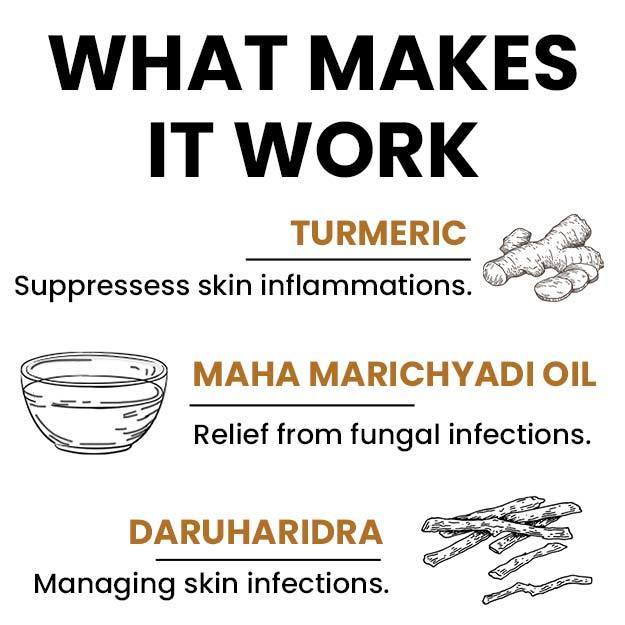
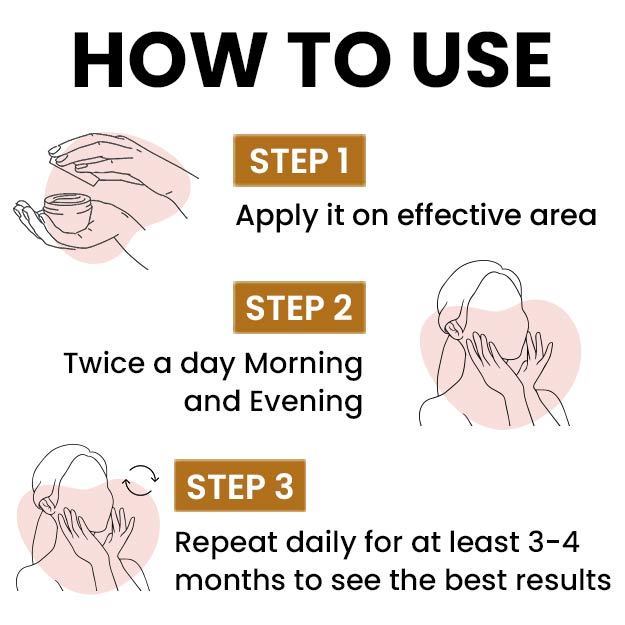
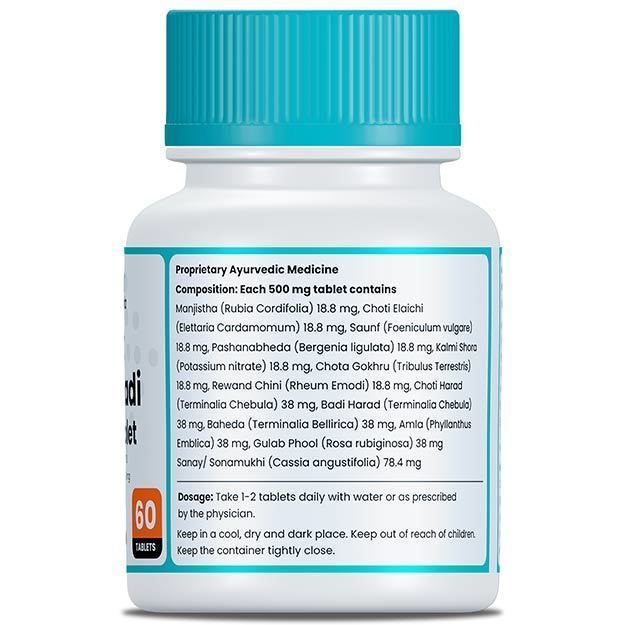
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Ringworm
Ayurvedic Treatment of Ringworm
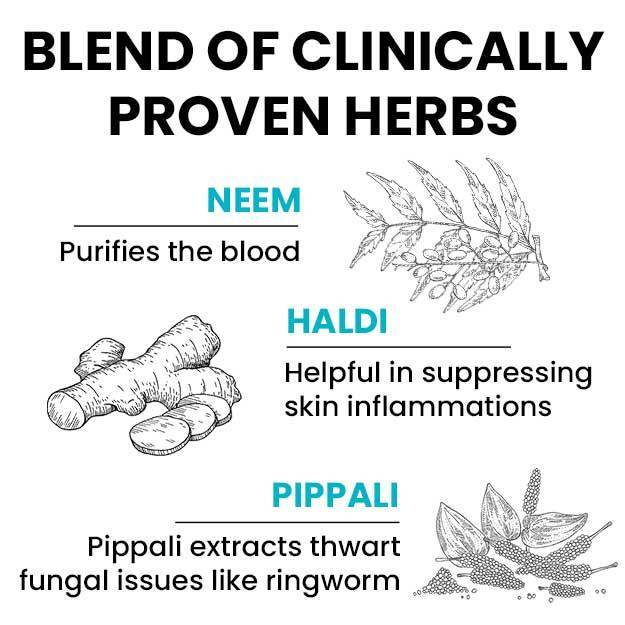
 Home Remedies for Ringworm
Home Remedies for Ringworm
 Homeopathic Treatment of Ringworm
Homeopathic Treatment of Ringworm






























 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
 Dr. Apratim Goel
Dr. Apratim Goel

 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria