In the year 1700, Italian physician Bernardino Ramazzini observed that workers in his country had been suffering from different types of stress injuries owing to their primary occupations. He went on to document their plight in his book Diseases of Workers. In the book, he categorised the stress injuries under as many as 20 headings!
Repetitive strain injuries (RSI) are a common phenomenon all over the world. Though modern lifestyles have made us more prone to some of these injuries, Ramazzini's book is proof that medical professionals have been thinking about ways to diagnose and treat RSIs for centuries.
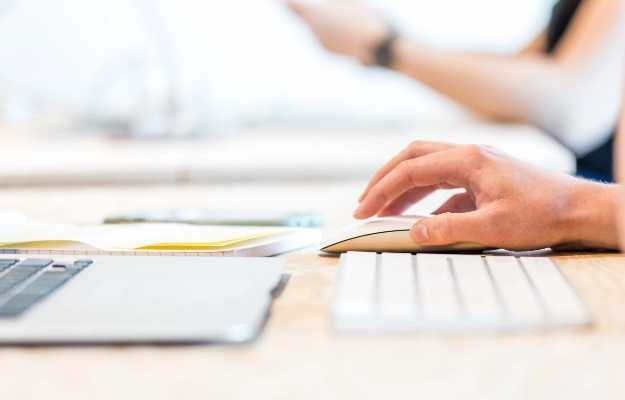
As the name suggests, RSIs are caused by repetitive movements. They are also known as repetitive motion disorders or repetitive stress injuries. Another common expression to describe RSI is overuse injuries. RSIs encompass several problems related to nerves, tissues, ligaments and tendons. Tendonitis (tendinopathy) and bursitis the most common forms of RSI.
While an RSI owes its origins to occupations such as manual labour, sports and harsh working environments, its more recent iterations have come from the use of modern technology. Conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome, PlayStation thumb and Blackberry thumb, Rubik’s or raver’s wrist are some of the modern RSI conditions that have developed over the years due to the use of technology.
The most basic of movements, like jogging in the morning or even typing on a computer, can result in RSIs. Though RSIs can affects the knees and ankles, a majority of such injuries are seen in the upper body - in the elbows, wrists or anywhere in the arm, as well as the shoulders and neck.

 Doctors for Repetitive stress injury
Doctors for Repetitive stress injury