Summary
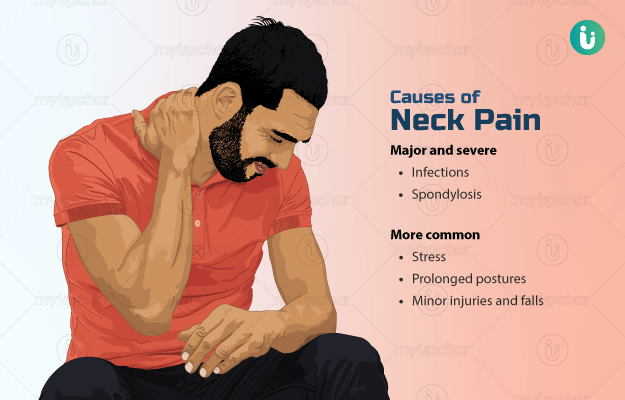
Neck pain is a common health problem with one in three people reporting it. The cause may be as simple as a strain in the muscles of the neck or a serious one, such as the compression of the nerves of the spinal cord. Diseases of the vertebrae (bones of the spine), arthritis, cervical spondylosis and other such conditions may also lead to neck pain and require immediate medical attention. People who are at a higher risk of developing neck pain include women, especially those having more than one child, and people with poor health. Neck pain due to a whiplash (that generally occurs during an accident) may show symptoms for years. The treatment of neck pain varies greatly and depends upon its underlying cause. Most of the times, neck pain resolves within a week. Rarely, it may last for years. Exercise, medication, and posture correction are the main treatment strategies employed for the management of neck pain. Surgery is generally not the first treatment option and is avoided until all options have been exhausted. For chronic neck pain, a multi-pronged approach is employed comprising of exercises, muscle strength training, medication, and lifestyle changes.

 Doctors for Neck Pain
Doctors for Neck Pain  OTC Medicines for Neck Pain
OTC Medicines for Neck Pain
 Neck Pain articles
Neck Pain articles
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Neck Pain
Ayurvedic Treatment of Neck Pain
 Exercise for Neck Pain
Exercise for Neck Pain
 Home Remedies for Neck Pain
Home Remedies for Neck Pain
 Homeopathic Treatment of Neck Pain
Homeopathic Treatment of Neck Pain



































 Editorial Team
Editorial Team

 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria
 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla












