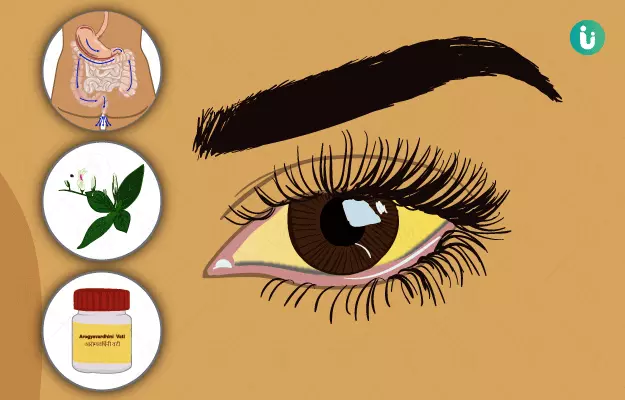
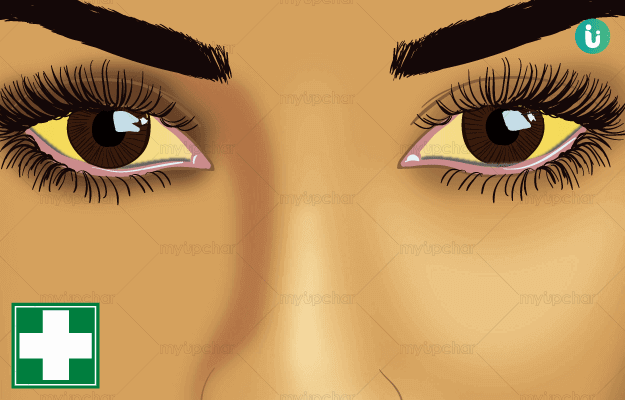
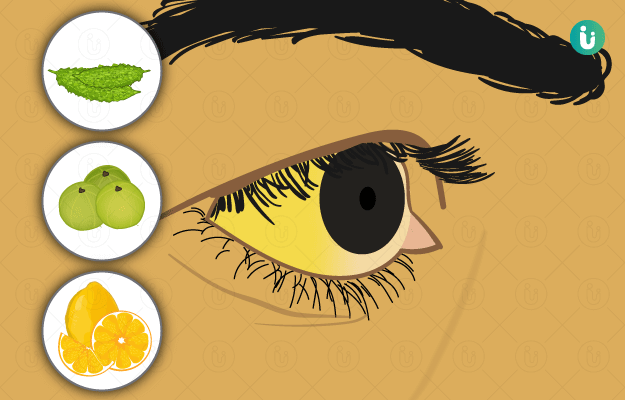
Jaundice is a liver disease that is caused due to excess levels of bilirubin, a pigment present in the body. The most commonly observed jaundice symptom is yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes. Excessive bilirubin levels can either be inherited or acquired. Inherited factors that are responsible for jaundice include glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency and acquired factors include trauma and vitamin B 12 deficiency. Jaundice is diagnosed by measuring the bilirubin level in plasma. Consuming low-fat meals and plenty of water can help manage jaundice.
(Read more: How many glasses of water to drink in a day)
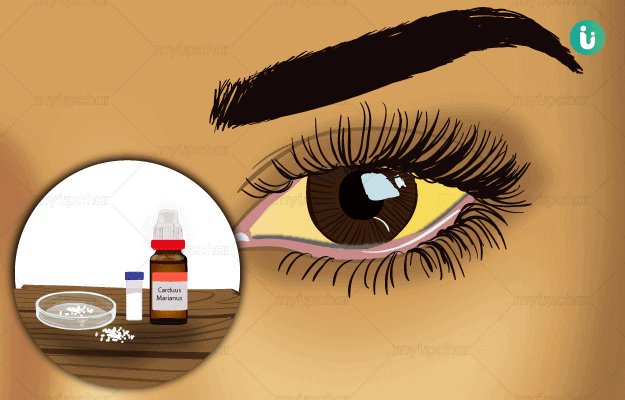
Jaundice is classified into three types based on the cause: pre-hepatic jaundice, hepatic jaundice and post-hepatic jaundice. Ayurvedic treatments have been traditionally used to treat various types of liver disorders successfully, including all types of jaundice, and even now, more than 50% of the Indian population relies on Ayurveda for the treatment of liver diseases. This is because toxicity levels of medications used in Ayurveda are low as compared to conventional medicines. Plenty animal and clinical research are now available to prove the effectiveness and safety of herbo-mineral and medicinal plants in treating liver diseases. One of the Ayurvedic medicines highly advocated for liver diseases is arogyavardhini vati (tablet), which also works on kamala (jaundice). Herbs like haridra (turmeric) and amalaki (Indian gooseberry) are some of the commonly used single herbs that are used to relive jaundice symptoms. Virechana (purgation), among all the five panchakarma (five treatments) procedures, is seen to be beneficial in treating jaundice.