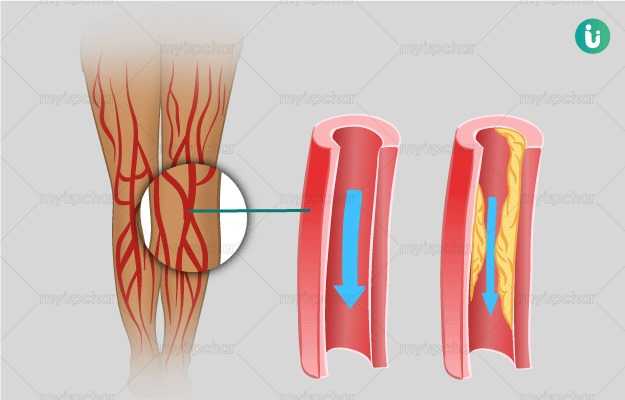
The word claudication literally means the state of being lame or limping. In medicine, claudication refers to severe and debilitating pain in the legs, thighs, hips or buttocks because of less-than-adequate blood flow to the region. Claudication can also occur in the arms, though this is rare.
A major symptom of peripheral arterial disease (PAD), claudication affects almost 20% of PAD patients. PAD itself is emerging as the third biggest cause of vascular morbidity worldwide, debilitating 200 million people.
Intermittent claudication occurs when a person walks or exercises - it subsides when they stop and the workload is taken off their lower extremities. However, as claudication progresses, the patient experiences pain and cramps in the peripheral limbs even during rest. Over time, the pain can become so bad that the person can’t even walk short distances.
Claudication usually occurs when there’s a blockage in the peripheral blood vessels. This reduces both blood flow and oxygen supply to the patient’s legs. Our muscles require up to 30 times more oxygen during exercise. In the absence of oxygen, various inflammatory mediators accumulate distal to the narrowed blood vessels, resulting in weakness, fatigue, pain, cramping, and inability to walk, that is, claudication.

 Doctors for Claudication
Doctors for Claudication