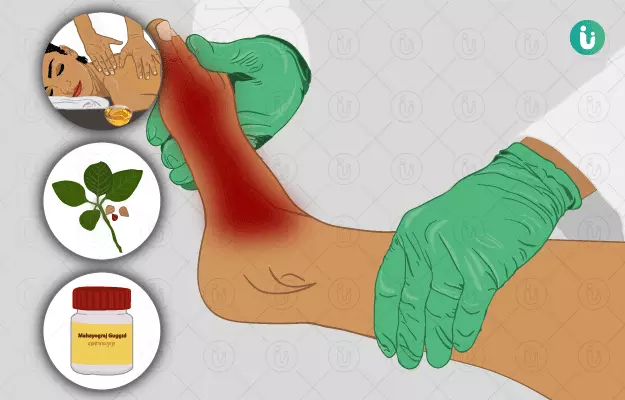
Foot pain is a common condition that may affect any part of the feet including heels, toes and ankles. While it may be caused due to sprain and factures, the three most common causes of foot pain are plantar fasciitis (severe heel pain), pain in the ball of the foot and overuse or inflammation in the achilles tendon (the largest tendon in the body that connects the heel bone and calf muscle). Health conditions like gout, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are some of the other causative factors of foot pain.
Panchakarma (five therapies) methods of basti (enema), virechana (purgation), snehana (oleation) and abhyanga (oil massage) are useful in reducing foot pain. Herbs like ashwagandha (Indian ginseng) and eranda (castor) along with herbal formulations of mahayogaraja guggulu, maharasnadi kwatha and kaishora guggulu are also used to treat the underlying causes of foot pain.
Including barley, clarified butter and green gram in the daily diet, avoiding sleeping during the daytime, maintaining correct posture, taking warm baths and performing massages can help achieve better and faster recovery from foot pain.