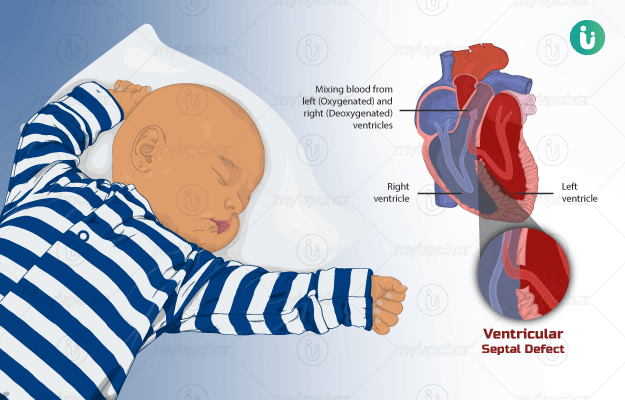
What is congenital heart disease?
Congenital heart diseases, or congenital heart defects, are among the most common structural defects involving the development of the heart or its blood vessels. A hole between the heart chambers (defect in the septal wall), narrowing of the main blood vessel of the heart (aorta) and pulmonary vein stenosis (narrowing of the vein of the lung) are some of the common congenital heart defects.
Here is the complete detail about heart disease treatment.
(Read More - Coronary Artery Disease)
What are its main signs and symptoms?
In adults, if left untreated and still persisting, certain symptoms may be seen, including:
- Shortness of breath (dyspnoea)
- Fatigue and exercise intolerance
In many cases, patients show very few or no signs and symptoms.
Signs and symptoms seen in severe cases include:
- Rapid breathing
- Excessive sweating
- Chest pain
- Cyanosis - skin, lips and fingernails appear bluish
- Fatigue
- Abnormal blood circulation
- Failure to thrive
- Poor feeding in babies due to dyspnoea
(Read More - Heart Attack treatment)
What are its main causes?
The most common causes are disturbances of the internal environment during early development of foetus inside the mother’s womb. Factors include:
- Infections
- Exposure of pregnant mother to harmful drugs
- Smoking or alcohol intake by pregnant mother
- Socio-demographic and environmental factors
Other causes include:
- Faulty genes and chromosomes
- Family history of congenital heart defects
- Parental illnesses also put child at risk of congenital heart defects
(Read More - Angina Treatment)
How is it diagnosed and treated?
- During pregnancy:
- Ultrasound scans may help detect congenital heart defects in the foetus. In some cases, this may be detected as early as 20 weeks.
- Antenatal (foetal) echocardiography is also useful in detecting congenital heart defects in the foetus.
- During childhood:
Proper diagnosis requires a thorough medical history and physical examination of the patient along with the following tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Chest X-ray
- Echocardiogram
- Pulse oximetry for screening
- During adulthood:
A number of diagnostic tests along with physical examination aid the doctor in detecting congenital heart defects in adults. These include:
- Echocardiogram
- Trans-oesophageal echocardiogram
- Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS)
- Cardiac catheterisation
- Chest X-ray
- ECG
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
Treatment of patients with congenital heart defects is decided by the severity of the defect and involves:
- No treatment
- Periodic check-ups by a cardiac specialist
- Medications which also include prophylaxis for endocarditis
- Invasive surgery for closure or repair of defects
(Read More - Enlarged Heart Treatment)

 OTC Medicines for Congenital Heart Disease (Defect)
OTC Medicines for Congenital Heart Disease (Defect)