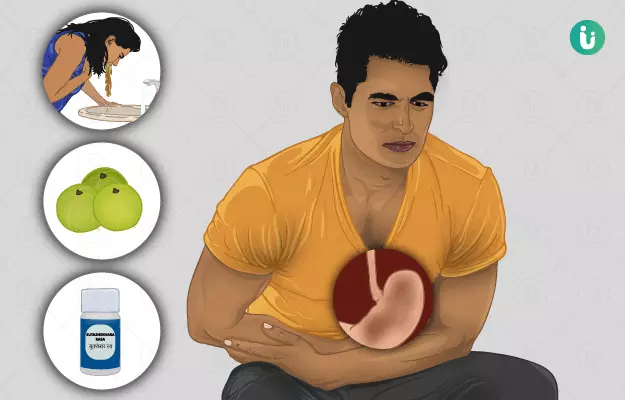
Acidity or heartburn is a common condition caused due to excessive production of stomach acids and irritation of gastric lining or food pipe due to this acid. It is usually experienced in the form of a burning sensation in the chest and stomach area after lying down, after eating, overeating, consuming alcohol or due to stress. It can last from a few minutes to a few hours. Health conditions like hiatal hernia (a state in which a part of the stomach is pushed upwards towards the chest), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and peptic ulcers also cause acidity.
Ayurveda terms acidity as amlapitta. As per Ayurveda, amlapitta is a disease of annavaha strotas (channels that transport, digest and absorb food). Ayurvedic doctors use shodhana (cleansing) methods such as virechana (purgation) and vamana (medical emesis) and shamana (pacification) methods such as langhana (fasting) and pachana (herbs to improve digestion) to treat acidity. Ayurvedic herbs like shunthi (dried ginger), yashtimadhu (mulethi) and amalaki (Indian gooseberry) help reduce acidity. Ayurvedic formulations of pravala panchamrita rasa, sutashekara rasa and avipattikar churna taken before or after meals promote better management of acidity. Addition of godhuma (wheat), mudga yusha (green gram soup) and exclusion of spicy foods, along with a limiting alcohol intake helps manage acidity.