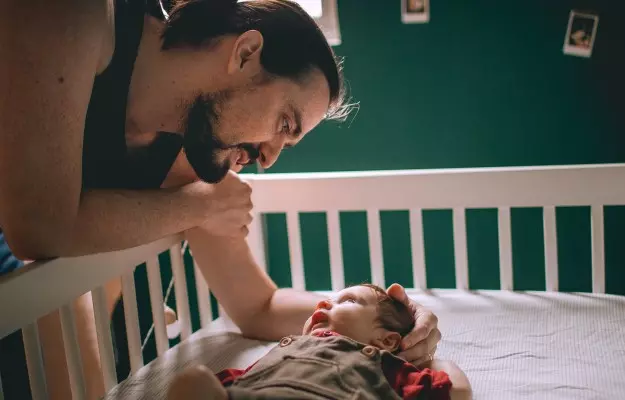
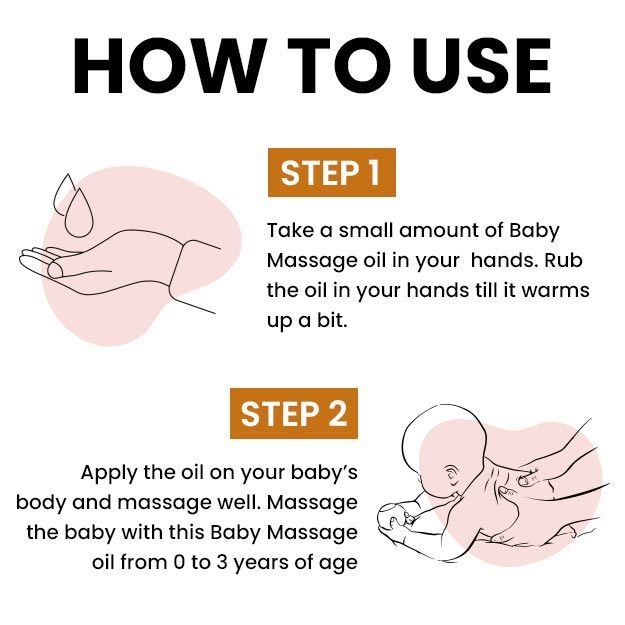
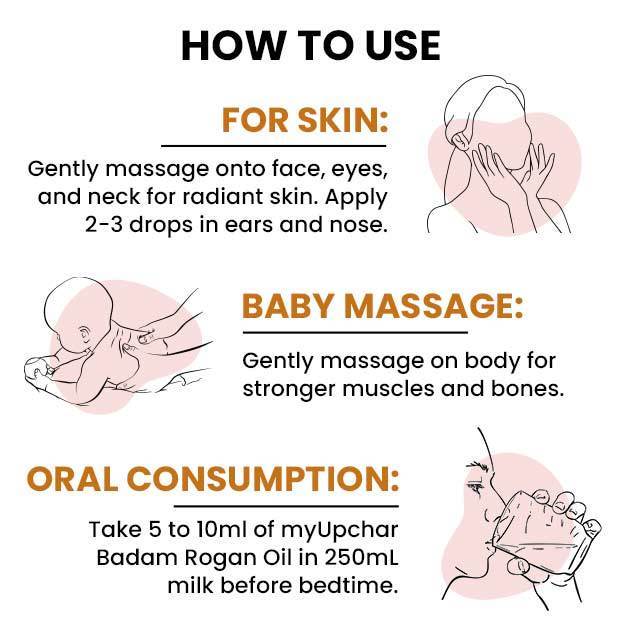
Roseola is an infection that affects most children between the ages of six months and two years. Once they have the infection, children develop antibodies for it - a second infection is extremely rare.
Also known as sixth disease, roseola is marked by high fever (103 degrees Fahrenheit or more) that can last for several days. A child who has contracted roseola may also get small pink rashes on the belly and back within a week or two of infection - doctors advise gently rolling a glass over the rashes to make sure they disappear under the slightest pressure (in case they don’t disappear with slight pressure, contact your paediatrician).
Two types of herpes virus - Human Herpesvirus 6 (HHV6) and rarely Human Herpesvirus 7 (HHV7) - cause this infection.
Roseola is a communicable disease - it spreads through contact with an infected person.
There is no particular season or time of year when the chances of getting roseola infection are higher. It can happen at any time of the year.