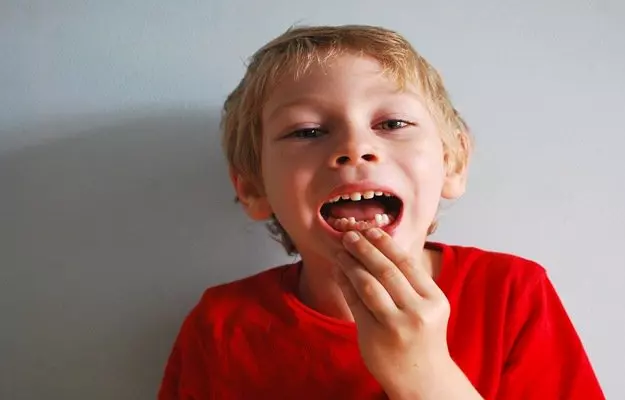
Teething or eruption of first milk teeth is a milestone in your child’s development. As a parent, it is always fascinating to watch those tiny little milk teeth to sprout out of the jaw bones. It’s a time of happiness as well as of some concern about how the teeth formation will be, What to do, and what not to do? Sometimes, you may get concerned when your child’s teeth do not erupt on time. Mostly, it is not of a major concern because your child’s teeth might just be following the pattern of your milk teeth eruption, i.e., if your teeth erupted late in your childhood, chances are that your child’s teeth will also have a slow pace of piercing through the gums. Hence, if your child’s teeth do not erupt even after one year of age, it is known as delayed tooth eruption. This is the time when you should go to a general dentist or a pedodontist (a dentist who specializes in children’s dental health) to find out the underlying cause of it.
There can also be a delay in the eruption of your adolescent’s permanent teeth. This is also associated with many local and general factors. If the teeth do not erupt till 6 months of the expected time of their eruption, you should take your child to a dentist to figure out the cause of it.