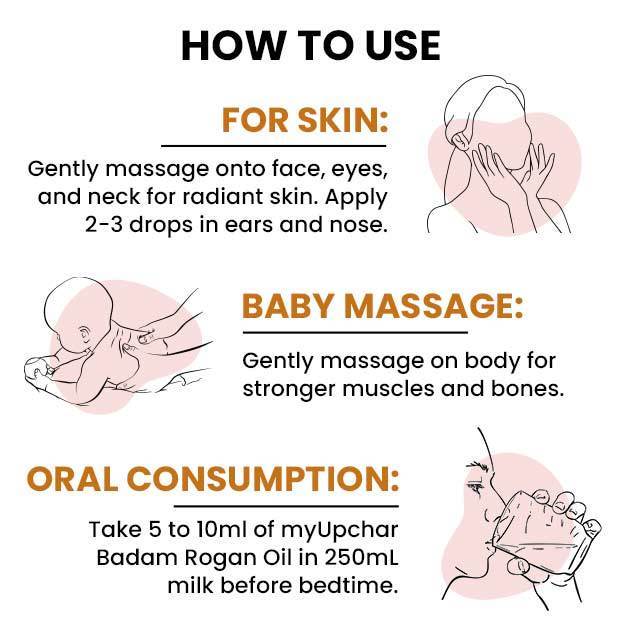
For all parents, a happy and healthy baby growing up right brings utter joy. Feeding the baby plays a huge role in this. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that all newborns should be exclusively breastfed for the first six months of life. This is primarily because breast milk has all the nutrients and fluids a baby needs to not just survive, but thrive, and with a fast-developing immune system too.
There are many other benefits of breastfeeding for both the mother and the child, which is why it’s recommended for all unless maternal health is compromised in a way that makes breastfeeding dangerous for the baby. Even if the mother gets an infection like COVID-19, it’s suggested the mother continue to provide breast milk for the baby by pumping milk during the crucial first six months. After the baby completes six months, solid foods can slowly be introduced to the baby.
Read more: Diet for breastfeeding mothers
This process of shifting the baby’s diet from breast milk to solid foods is known as weaning, and it’s considered to be a delicate and auspicious process in India—often marked by a ceremony where the baby is first fed mashed rice or kheer. Though the process of weaning begins at six months, it can take up to two years to completely wean the baby off breastfeeding and get him or her used to eating solid foods only.
Read more: How and when to stop breastfeeding your baby
It’s very important to remember that even though you should start introducing your baby to solid foods after six months, continuing with breastfeeding until the baby is completely weaned is very important—as important as sticking to the timetable of immunizations for the baby. Read this article to find out everything you need to know about weaning your baby through the introduction of solid foods.