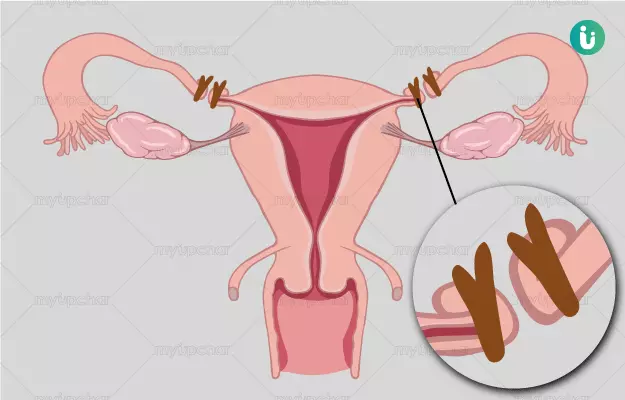
A woman’s reproductive system consists of external and internal sex organs. The external sex organs are labia majora, labia minora, Bartholin glands, and clitoris. The internal sex organs are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tube and ovaries. The ovaries make the eggs and send them to the uterus through the fallopian tubes. The sperms fuse with the eggs in the uterus and form the embryo.
Tubectomy is a surgical procedure to prevent pregnancy by blocking the fallopian tubes. Tubectomy is also known as tubal ligation, tubal sterilization and female sterilization. The surgery is minimally invasive and does not leave a big scar. Recovery is usually fast - women are often discharged as soon as the anaesthesia wears off. They can also resume sexual activity after about a week.
Tubectomy can be done for any woman who does not wish to get pregnant. The procedure is permanent (some places offer a procedure to reverse a tubectomy, but it is very difficult and there are no guarantees that reversing a tubectomy will restore fertility).